Çakaristan elections
Çakaristan elections are held at the national level for the Majlis al-Shuyukh and Majlis al-Nuwaab. The members of the Majlis al-Shuyukh are directly elected by the people of each division. The members of the Majlis al-Nuwaab are elected through national elections of proportional representation.
Previously, the Grand Vizier was elected by election through a system of electoral votes.
Cycle of elections
Various elections, both national and regional, are arranged in a cycle of elections. As a result, some biennial elections are held, but for different parts.
| Year 1 | Year 3 | Year 5 | Year 7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grand Vizier (suspended) | 1 | 1 | ||
| Majlis al-Shuyukh | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/3 |
| Majlis al-Nuwaab | all | all |
Years 1 and 5 are called a "Congressional election year" in this survey. Year 3 and 7 are called "Shuyukh election year", before the suspension of elections for Grand Vizier, this was called the "Grand Vizier election year".
Past elections
Majlis al-Sultina
In the first Çakar era, two elections of the then-called "Majlis al-Sultina" (Council of the Sultanate) were held:
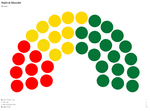
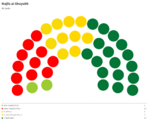
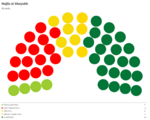
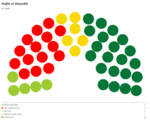
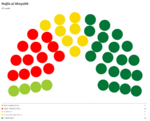
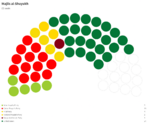
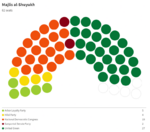
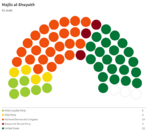
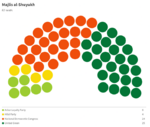
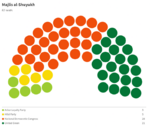
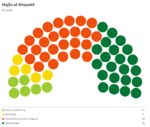
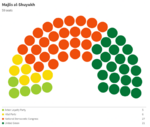
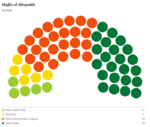
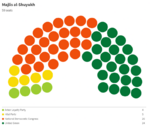
Majlis al-Shuyukh
Since the restoration of the Çakar Empire and establishment of the Akbar Constitution, the following elections for the Majlis al-Shuyukh were held:
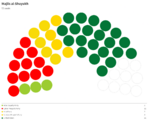
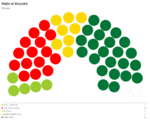
Majlis al-Nuwaab
Since the restoration of the Çakar Empire and establishment of the Akbar Constitution, the following elections for the Majlis al-Nuwaab were held:
Electoral process
The election process for the Grand Vizier, Majlis al-Shuyukh and Majlis al-Nuwaab is determined by the Akbar Constitution. Elections for the Governor and Governate or State Assembly are determined by separate regulations.
Electors
Electoral officers are used to elect the Grand Vizier. In each governorate, riyasat and subah, the number of electors is equal to the number of Shuyukh. There is one elector per sarkar. Once the votes for the Grand Vizier have been cast, the electors will put their votes in writing. This is sent to the Chairman of the Majlis al-Shuyukh, who counts all the votes cast in a special session. If no majority is obtained by one of the candidate Grand Viziers, the Majlis al-Nuwaab will vote on the candidates.
Electoral constituency
The members of the Majlis al-Nuwaab are elected by a list system for each electoral constituency. Each governorate, riyasat, subah and sarkar constitutes a constituency. These constituencies can be further divided into several constituencies with a minimum size of 300,000 free citizens per seat. The boundaries of the electoral constituencies are determined by the governorate, riyasates, subahs or sarkars themselves.
The constituencies are calculated on the total number of free citizens per governorate, riyasat, subah and sarkar. It is expected that with the detailed implementation of constituencies, the number of constituencies will be reduced and thus the number of seats in the Majlis al-Nuwaab.
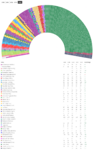
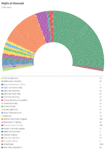
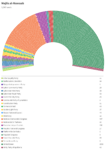
Overview
The following chart shows the number of electors, Shuyukh, and seats in the Majlis al-Nuwaab:
| Abbr. | Electors | Shuyukh | Seats of Majlis al-Nuwaab | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agra | DA | 1 | 37 | |
| Aurangabad | AU | 1 | 0 | |
| Barikalus | BA | 6 | 6 | 221 |
| Beneluccas | BE | 1 | 2 | |
| Bulqan | BU | 3 | 3 | 153 |
| Haritdesh | HD | 6 | 6 | 2,680 |
| Jaguda | JA | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Kadim | KA | 1 | 4 | |
| Kantisha and Northak Islands | KN | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Kendall Khanate | KK | 6 | 6 | 326 |
| Korhalistan | KO | 6 | 6 | 357 |
| Kyazilkai | KY | 6 | 6 | 22 |
| Leyl Sadarya | LE | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Lija | LI | 1 | 0 | |
| Micabad | MA | 0 | 0 | |
| Nuristan | NU | 3 | 3 | 15 |
| Oceanic Territory | OT | 1 | 0 | |
| Pathaardesh | PD | 0 | 59 | |
| Poorajangal | PJ | 3 | 3 | 203 |
| Sikatadesh | SD | 1 | 1 | 145 |
| Sri Pashana | SP | 6 | 6 | 152 |
| Sunehra | SU | 1 | 1 | 116 |
| Suqutra | SQ | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Sylfystan | SY | 3 | 3 | 65 |
| Tartaristan | TA | 1 | 22 | |
| Tennyn | TE | 0 | 0 | |
| Valesia | VA | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Vashigol | VG | 0 | 5 | |
| Total | 64 | 56 | 4,594 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||