Helderbourgh
| Grand Duchy of Helderbourgh | |||
| |||
| Motto: Prospice Hellebergh | |||
| Anthem: Mountain Men (Unofficial) | |||
| |||
| Map versions | 6.8.3 - 6.8.5; 7.0.0 - 7.0.1; 14.9.4 - present | ||
| Capital | Helderbourgh Stadt | ||
| Largest city | Helderbourgh Stadt
| ||
| Official language(s) | English, Dutch The latter is primarily ceremonial | ||
| Official religion(s) | Holy Catologian Church | ||
| Demonym | Helderbourgers | ||
| - Adjective | Helderbourgish | ||
| Government | Monarchy | ||
| - Grand Duke | Arkadius Frederik Gustavus des Vinandy | ||
| - None | None | ||
| - Legislature | 'Assembly of Estatesl | ||
| Establishment | 12 Winter month 1667 AN (12 December 2018) | ||
| Area | 9,728,732 km² | ||
| Population | 18,589,247 | ||
| Active population | 1 | ||
| Currency | Heldermark | ||
| Calendar | |||
| Time zone(s) | CMT-11 | ||
| Mains electricity | |||
| Driving side | right | ||
| Track gauge | |||
| National website | None | ||
| National forum | forum | ||
| National animal | Siebenbergen Goat | ||
| National food | None | ||
| National drink | Birch Beer | ||
| National tree | Pitch Pine | ||
| Abbreviation | HLB | ||
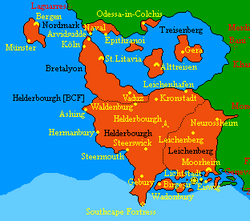
Helderbourgh, officially Grand Duchy of Helderbourgh (Batavian: Groothertogdom Helderburg), is a wikibased country in the southwest of Cibola. With an area of 9,728,732 km² and with more than fifteen million inhabitants, the grand duchy is the largest country on the Cibola continent. The capital and largest city of the country is the eponymous Helderbourgh Stadt.
Currently, the country does not share a national border with another nation. To the south of the mainland are some islands of Natopia. To the west, the land borders on the Eastern Sea, to the north on the Central Sea of Cibola. In this inland sea the country includes the three islands. It is green to the east of the country. There are expansion plans for some coastal areas north of the inland sea and the island northwest of the current country, these parts belonged to the historic Eternal Realm of Treisenberg.
Helderbourgh is a parliamentary democracy with a grand duke as a constitutional monarch. Since 1672 AN Arkadius Frederik Gustavus des Vinandy has been the grand duke, creating a de facto personal union with Batavia and the Frankish Empire. In the same year, Helderbourgh became a member of the Batavian Confederation. In 1673 AN, Helderbourgh was incorporated as an autonomous area of the Kingdom of Batavia.
Etymology
The original name of Helderbourgh is Helderburg. The name Helderburg consists of two Batavian words: helder (bright) and burg (bourg or castle). An extra "h" is added to the spelling of bourg.
When the city of Helderbourgh, later Helderbourgh Stadt, became the capital of the country, that name was used for the country. The name of the city is in turn derived from the location on the mountain, the Helderberg (bright mountain).
History
Predecessors
The current grand duchy sees itself as a continuation of the following historical states:
 Federal Republic of Germania
Federal Republic of Germania Eternal Realm of Treisenberg
Eternal Realm of Treisenberg Duchy of Rossheim-Slavonia-Volksburg
Duchy of Rossheim-Slavonia-Volksburg- United States of the Sangunese Crown
 Kingdom of Greater Sangun
Kingdom of Greater Sangun- Principality of Rossheim
- Kingdom of Riskai
 Kingdom of Sangun, Riskai and the Idunn Isles
Kingdom of Sangun, Riskai and the Idunn Isles Kingdom of Sangun and Riskai
Kingdom of Sangun and Riskai- Grand Duchy of Riskai
 Empire of Greater Sangun
Empire of Greater Sangun Sangun-Treisenberg
Sangun-Treisenberg Cibolan Confederation
Cibolan Confederation Kingdom of Leichenberg
Kingdom of Leichenberg Sanguno-Leichbergish Union
Sanguno-Leichbergish Union Empire of Sangun and South Cibola
Empire of Sangun and South Cibola Empire of Minarboria
Empire of Minarboria United Kingdom of Steeria and Highfield
United Kingdom of Steeria and Highfield United Principalities of Treisenberg
United Principalities of Treisenberg
Current Grand Duchy
Prior to becoming a major city, Helderbourgh was a small village consisting of a few families of Treiso-Batavian descent. These original settlers hailed from Batavian Cibola, some two to three thousand years ago, when Batavia held colonies in what is presently Bretalyon. Over time these families intermarried with the Germanian population, and these families settled and named the Helderbergs.
Helderbourgh arose as a result of a protracted civil war within the United Principalities of Treisenberg. During the events of the White Plague, Treisenberg's principalities began to war with one another. In particular they came into conflict with the fanatical crusaders of Bretalyon. Helderberg Mountain became a refuge for those escaping the pillage wrought by the Knights. Soon the number of refugees became so great that the village and then city of Helderbourgh arose on the mountaintop. After the Grand Commander of the Knights was assassinated, the Bretalois sued for peace and the country was reorganized. With many cities utterly destroyed and others still in flames, Helderbourgh became the new center of the country.
In 1672 AN Arkadius Frederik Gustavus des Vinandy was named Grand Duke and the country joined the Batavian Confederation. Then in 1673 AN, Helderbourgh became an autonomous area of the Kingdom of Batavia.
Geography

Central Helderbourgh is dominated by the most southwestern mountain (called Helderberg Mountain) of the seven mountains on Cibola. The name in Batavians is Zevenbergen or in Germanian Siebenbergen (seven mountains). The region is typified by several tall mountains that punctuate the central regions of Cibola, with a steeply declining elevation in terrain down to the surrounding ocean. Because of this drastic change in elevation the climate between different areas can vary significantly. Mountainous regions favour a mostly alpine climate, with the upper peaks often capped with permanent snow.
The Central Sea of Cibola (Batavian: Zeetuinen, Germanian: Meergarten) has a more Mediterranean to temperate climate.
Flora and fauna
Cibolan Daffodil

The Cibolan Daffodil (Narcissus cibolus) is a native wild daffodil common to the southern half of Cibola. It is a perennial plant that grows from a bulb and flowers annually. The plants grow best in grasslands and rocky ground, but will also grow under the cover of a light forest canopy. Cultivation of the Cibolan Narcissus has been a pastime of Treisenbergers for centuries, and an international market for the sale of bulbs has grown over the past two-hundred years. A large number of hybrids now exist thanks to the breeding of specialty cultivars.
Siebenbergen Goats

The Siebenbergen Goats (Capra ibex), also known as the steinbock, is a species of wild goat that lives in the mountains of Cibola. It is a sexually dimorphic species with larger males that carry larger, curved horns. Their coat colour is typically brownish grey. Siebenbergen Goats tend to live in steep, rough terrain near the snow line. They are also social, although adult males and females segregate for most of the year, coming together only to mate. Four distinct groups exist; adult male groups, female-offspring groups, groups of young individuals, and mixed-sex groups. During the breeding season, males fight for access to females and use their long horns in agonistic behaviours.
Government


Helderbourgh is a parliamentary democracy headed by a constitutional monarch. This is established in the Basic law of the Grand Duchy of Helderbourgh.
Executive power is exercised by the Grand Duke and his Cabinet. The Grand Duke has the power to dissolve the legislature, in which case parliamentary elections must be held within three months.
Legislative power is vested in the Assembly of Estates which is composed of sixteen representatives, four from each of the four cantons (Helderbourgh, Treisenberg, Bretalyon and Leichenberg).
The Grand Duchy has several lower Tribunals, one for the Supreme Court, one for State, one for Defense, and one for Internal Affairs.
Cantons
| Flag | Canton | Capital |
|---|---|---|
| Bretalyon | St. Litavia | |
| Canton Helderbourgh | Helderbourgh Stadt | |
| Leichenberg | Moorheim | |
| Treisenberg | Alttreisen |
Crown Cantons
The crown cantons are special regions under direct management and owned by Arkadius Frederik Gustavus des Vinandy. As long as he is Grand Duke, these regions are part of Helderbourgh.
| Flag | Crown Canton | Capital |
|---|---|---|
| Nederburg | Herckenburg | |
| Nordmark | Bergen |
Demographics
The total population of Helderbourgh is 18,589,247. The population growth in 1675 was 3.7%. Overview of the population groups:
| 1667 | 1668 | 1669 | 1670 | 1671 | 1672 | 1673 | 1674 | 1675 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bretalois | 3,000,000 | 3,072,000 | 3,145,728 | 3,249,537 | 3,337,275 | 3,480,777 | 3,654,816 | 3,768,115 | 3,907,536 |
| Helderbourghers | 5,271,844 | 5,398,368 | 5,527,929 | 5,710,351 | 5,864,530 | 6,116,705 | 6,422,540 | 6,621,639 | 6,866,640 |
| Leichenbergers | 2,500,000 | 2,560,000 | 2,621,440 | 2,707,948 | 2,781,062 | 2,900,648 | 3,045,680 | 3,140,096 | 3,256,280 |
| Treisenbergers | 3,500,000 | 3,584,000 | 3,670,016 | 3,791,127 | 3,893,487 | 4,060,907 | 4,263,952 | 4,396,135 | 4,558,792 |
Culture
Helderbourgh is a land dominated by the mountains of Cibola. As such the region has developed a distinct Alpine culture with influences from preceding nations such as Germania, Batavia and others.
Economy
Helderbourgh has a stable economy and has rebounded well since the end of the civil war. Industrial manufacturing is the largest sector of the economy, thanks in part to ample access to various metal ores in the mountains. The country is also a major producer of gold exports, having one of the largest gold mines on Micras. The majority of mining and industrial factories are located in the eastern region of the country, primarily in Leichenberg. A strong rail network links the hill town industrial centers to the main port, Leichenhafen, and transport to the world markets is through Treisenberg's sizable shipping network.
The region of Helderbourgh is known for tourism and its extensive fruit growing. This includes apple orchards and vineyards, which are suitable for the hilly terrain. The flatlands of Bretalyon are mostly agricultural, and serve as the main supplier of foodstuffs for the country. The southern polar reaches are sparsely populated and more of a subsistence economy.
Gold
Many gold concentrations can be found in the mountains of Helderbourgh. This makes Helderbourgh a global player in the gold trade. The Batavian Trading Company has the concession for the export of gold.
Military
The army is considered a civilian operation, with the Grand Duke serving as Commander-in-Chief. The Minister of Defense oversees military operations, while individual chiefs for the army, navy and air force each report to the minister.
Southcape (Sudkap) Fortress serves as the largest military installation and headquarters for the Helderbourger military. Several other smaller bases provide regional defense. The navy is headquartered at Alttreisen.
| |||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


