Oportia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
|flag = File:Oportia flag.png | |flag = File:Oportia flag.png | ||
|coa = File:Oportia_coat_of_arms.png | |coa = File:Oportia_coat_of_arms.png | ||
|motto = ''Liberté avant tout''<br>''Oportet'' | |motto = Official: ''Liberté avant tout''<br>Informal: ''Oportet'' | ||
|anthem = ''[[Le bateau]]'' | |anthem = ''[[Le bateau]]'' | ||
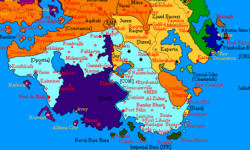
|map = File: | |map = File:Oportia1733Map.png | ||
|mapversions = 17.5.7 – | |mapversions = 17.5.7 – | ||
|capital = [[Vanie]] | |capital = [[Vanie]] | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
|govtype = [[wikipedia:Constitutionality|Constitutional]] [[wikipedia:Federal republic|federal republic]] under [[wikipedia:Semi-direct democracy|semi-direct democracy]] | |govtype = [[wikipedia:Constitutionality|Constitutional]] [[wikipedia:Federal republic|federal republic]] under [[wikipedia:Semi-direct democracy|semi-direct democracy]] | ||
|headofstatetitle = [[Federal Representative of Oportia|Federal Representative]] | |headofstatetitle = [[Federal Representative of Oportia|Federal Representative]] | ||
|headofstate = [[ | |headofstate = [[Galilea Montijo]] ([[Liberty Now! Movement]]) | ||
|headofgovernmenttitle = [[Federal Chancellor of Oportia|Federal Chancellor]] | |headofgovernmenttitle = [[Federal Chancellor of Oportia|Federal Chancellor]] | ||
|headofgovernment = [[ | |headofgovernment = [[Emmanuel Aubin]] ([[Liberty Now! Movement]]) | ||
|legislature = [[Federal Congress of Oportia]] | |legislature = [[Federal Congress of Oportia]] | ||
|estdate = {{AN|1706}} | |estdate = {{AN|1706}} | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
|abbrev = OPO, OP | |abbrev = OPO, OP | ||
}} | }} | ||
The '''State of Oportia''' ([[Académie Alexandrin|Alexandrian]]: '''''L'État d'Oportie''''') is a constitutional federal republic in southern [[Eura]], known for its unique system of semi-direct democracy and strong civil liberties. Founded in {{AN|1706}} through the union of several autonomous city-states under the [[Compagnie Generale d'Oportia]] in [[Eura]], Oportia has developed into a significant regional power, with its capital at [[Vanie]]. The nation operates under a four-branch system of government that includes the executive, legislative, judicial, and the [[Federal Electorate of Oportia|Federal Electorate]], a novel democratic institution comprising all registered voters that serves as a direct check on governmental power. | |||
Since its establishment, Oportia has emerged as a notable example of democratic governance, ranking first in the [[Micras Democracy Index]] in {{AN|1707}} with maximum scores in political participation and civil liberties. The country underwent significant political reform in {{AN|1722}} following the [[1721 Oportian protests]], transitioning from its First Republic to the current Second Republic, which strengthened democratic institutions and established a bicameral legislature. This period also saw the implementation of major economic reforms, including the introduction of a progressive taxation system and expanded public infrastructure programs. | |||
Oportia's political alignment has evolved substantially over time, moving from membership in the [[Xäiville Convention]] ({{AN|1719}}-{{AN|1729}}) to joining the [[Raspur Pact]] in {{AN|1729}}. Under the leadership of Federal Representative [[Galilea Montijo]], the country has experienced rapid economic growth, driven by the exploitation of [[Alexandrium]] deposits and aggressive export-oriented policies. The nation maintains a diverse linguistic landscape, with [[Alexandrian language|Alexandrian]] and [[Istvanistani language|Istvanistani]] as federal languages, while regional languages include [[Babkhi language|Babkhi]], [[Pallisican language|Pallisican]], [[wikipedia:Romanian language|Sarnechi]], [[Yamaqhacha people#Language|Shahvekh]], and [[Thraci language|Thraci]], reflecting its multicultural heritage and immigrant population. | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
{{Main|History of Oportia}} | {{Main|History of Oportia}} | ||
===Formation=== | |||
* {{AN|1690}}-{{AN|1705}}, Background: | * {{AN|1690}}-{{AN|1705}}, Background: | ||
** Tied to the formation of [[Altus]] and [[Alduria]] (all the way back). | ** Tied to the formation of [[Altus]] and [[Alduria]] (all the way back). | ||
| Line 56: | Line 54: | ||
*** Formation of Oportian political culture: consensus-building, compromise, direct democracy, liberty, etc. First political organizations are formed: Jean Nouel founds the [[Conservative Nationalist Party of Oportia]], Laurent Morsi founds the [[Liberal Progressive Party of Oportia]]. Soon, in the [[Alexandria|Alexandrian]] tradition, divergent movements began to form with Léa Dubois founding the [[Green Party of Oportia]], and François Delacroix founding the [[Worker's Unity Party of Oportia]]. Sophie Marchand, independent but a [[Nationalist & Humanist Party|Humanist]] sympathizer, caught some fire but did not progress too far. Seen as eccentric but honest. [[wikipedia:Martha_Mitchell#Public_image|Martha Mitchell]] type of lady. Later on she founds the [[Nationalist & Humanist Party|Nationalist & Humanist Party of Oportia]] in {{AN|1729}} as the [[Conservative Nationalist Party of Oportia]] splits over Oportia leaving the [[Xaiville Convention]] and joining the [[Raspur Pact]]. | *** Formation of Oportian political culture: consensus-building, compromise, direct democracy, liberty, etc. First political organizations are formed: Jean Nouel founds the [[Conservative Nationalist Party of Oportia]], Laurent Morsi founds the [[Liberal Progressive Party of Oportia]]. Soon, in the [[Alexandria|Alexandrian]] tradition, divergent movements began to form with Léa Dubois founding the [[Green Party of Oportia]], and François Delacroix founding the [[Worker's Unity Party of Oportia]]. Sophie Marchand, independent but a [[Nationalist & Humanist Party|Humanist]] sympathizer, caught some fire but did not progress too far. Seen as eccentric but honest. [[wikipedia:Martha_Mitchell#Public_image|Martha Mitchell]] type of lady. Later on she founds the [[Nationalist & Humanist Party|Nationalist & Humanist Party of Oportia]] in {{AN|1729}} as the [[Conservative Nationalist Party of Oportia]] splits over Oportia leaving the [[Xaiville Convention]] and joining the [[Raspur Pact]]. | ||
** Tie in regional history, background, and development with [[Zeed]], [[Constancia]], and [[Suren Confederacy]]. | ** Tie in regional history, background, and development with [[Zeed]], [[Constancia]], and [[Suren Confederacy]]. | ||
===First Republic (1706-1722)=== | |||
* {{AN|1706}} The State of Oportia is founded. (First Republic) | * {{AN|1706}} The State of Oportia is founded. (First Republic) | ||
** Led by [[Jean Nouel]], the [[Declaration of Vanie]] founds and proclaims the independence of Oportia. Union of different city states each started by different settlement companies. All form together and approve a Constitution that will be ratified in a national referendum, assembly first Federal Cabinet. | ** Led by [[Jean Nouel]], the [[Declaration of Vanie]] founds and proclaims the independence of Oportia. Union of different city states each started by different settlement companies. All form together and approve a Constitution that will be ratified in a national referendum, assembly first Federal Cabinet. | ||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
** Jean dies in office from a heart attack in {{AN|1712}}. | ** Jean dies in office from a heart attack in {{AN|1712}}. | ||
** Jean is succeeded by [[César André]] who completes his Jean's term and gets elected in his own right in {{AN|1714}} | ** Jean is succeeded by [[César André]] who completes his Jean's term and gets elected in his own right in {{AN|1714}} | ||
** Territorial expansions during this time, why did they happen,. how they impacted Oportia. | |||
** (XIV.1709 AN and III.1710) [[Yamaqhachan insurgency]]. | |||
** (22.XIV.1716) [[Souduraine clash]]. | |||
** [[César André]] serves until the [[1721 Oportian protests]] have him and his party removed in the [[Oportia emergency national referendum, 1721]]. | ** [[César André]] serves until the [[1721 Oportian protests]] have him and his party removed in the [[Oportia emergency national referendum, 1721]]. | ||
** [[Celine Beaumont]] installed as caretaker [[Federal Representative of Oportia]]., caretaker government installed until general elections in early {{AN|1722}} | ** [[Celine Beaumont]] installed as caretaker [[Federal Representative of Oportia]]., caretaker government installed until general elections in early {{AN|1722}} | ||
** The transformation into a federal republic followed [[Oportian special national referendum, 1722|a national referendum]] in {{AN|1722}}, alongside the [[Oportian special general election, 1722|Oportian special general election]]. | |||
===Second Republic (1722 - Now)=== | |||
** The transformation into a federal republic followed [[Oportian special national referendum, 1722|a national referendum]] in {{AN|1722}}, alongside the [[Oportian special general election, 1722|Oportian special general election]]. This is generally considered as the end of the First Oportian Republic and the start of the Second Oportian Republic. | |||
* Second Republic (1722-Now) | |||
** [[Celine Beaumont]] is elected in her own right as Federal Representative in 1722 and 1726. Rise of the [[Liberal Progressive Party of Oportia]]. | |||
** Oportian economic crisis, Oportia joins the [[Euran Economic Union]], gets rescue package from the EEU and Natopia. | |||
** Oportian economic recovery, territorial expansion, continued reforms, Oportian Defense Review 1723, political and domestic events, etc. | |||
** Oportia leaves the Xaiville Convention and joins the Raspur Pact. | |||
** 1730 general elections: [[Celine Beaumont]] is ineligible to run for re-election a third time due to the limitations of the Oportian Constitution. | |||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
| Line 72: | Line 83: | ||
==Government and politics== | ==Government and politics== | ||
{{Main|Government and politics of Oportia}} | {{Main|Government and politics of Oportia}} | ||
The | The State of Oportia operates as a constitutional republic under a system of representative democracy that incorporates elements of direct democracy through the [[Federal Electorate of Oportia|Federal Electorate]], a unique fourth branch of government. This structure allows for a balanced distribution of power among the executive, legislative, and judicial branches, while ensuring that the citizenry has a direct voice in the governance process. | ||
===Constitution=== | ===Constitution=== | ||
The new Constitution, established in {{AN|1722}}, balances powers between the federal and city levels | The new Constitution, established in {{AN|1722}} as a result of the [[1721 Oportian protests]] and subsequent reforms, balances powers between the federal and city levels. It introduced a bicameral representative legislature while keeping the [[Federal Electorate of Oportia]], tipping the balance in favor of more representative democracy. Key aspects of the Constitution include political neutrality for a greater amount of public offices, environmentalism, and expanded human rights protections. | ||
====Executive==== | ====Executive==== | ||
The Head of State is the [[Federal Representative of Oportia|Federal Representative]], who presides over the [[Federal Cabinet of Oportia|Federal Cabinet]]. | {{Main|Federal Representative of Oportia}} | ||
{{Main|Federal Cabinet of Oportia}} | |||
{{Main|Federal Chancellor of Oportia}} | |||
The Head of State is the [[Federal Representative of Oportia|Federal Representative]], who presides over the [[Federal Cabinet of Oportia|Federal Cabinet]]. The [[Federal Chancellor of Oportia]] acts as the Deputy, with specific reserved powers over foreign affairs and special responsibilities. | |||
====Legislature==== | ====Legislature==== | ||
The [[Federal Congress of Oportia]] is the | {{Main|Federal Congress of Oportia}} | ||
{{See also|Chamber of Deputies of Oportia}} | |||
{{See also|Senate of Oportia}} | |||
The [[Federal Congress of Oportia]] is the bicameral representative legislature of Oportia, divided into two chambers: the lower chamber (and most powerful), the [[Chamber of Deputies of Oportia]], and the upper chamber, the [[Senate of Oportia]]. Federal Congress has constitutionally reserved powers that include proposing and voting on laws, political appointments, policies, and public initiatives. | |||
====Federal Electorate==== | |||
{{Main|Federal Electorate of Oportia}} | |||
The [[Federal Electorate of Oportia]] comprises all registered voters in Oportia, functioning as a fourth branch of government. This body has the power to propose legislation, call for referendums on critical issues, and directly participate in decision-making processes that affect national policy. The Federal Electorate ensures that Oportia's democracy is vibrant, participatory, and responsive to the will of the people. | |||
====Judiciary==== | ====Judiciary==== | ||
The [[Federal High Court of Oportia|Federal High Court]] is the highest court, overseeing violations of the | The [[Federal High Court of Oportia|Federal High Court]] is the highest court, overseeing violations of the [[Constitution of Oportia]] and federal law. | ||
===Foreign | ===Foreign Relations=== | ||
====Raspur Pact==== | |||
===Law enforcement and military=== | ===Law enforcement and military=== | ||
{{Main|Oportian Security Forces}} | {{Main|Oportian Security Forces}} | ||
The [[Oportian Security Forces]] | The [[Oportian Security Forces]] encompass civilian police services, military units, and special operations forces, maintaining internal security, defending national sovereignty, and contributing to international peacekeeping efforts. Structured to respond to a variety of challenges, the Security Forces operate under strict oversight to ensure they adhere to democratic principles and respect for civil liberties. | ||
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
{{Main|Economy of Oportia}} | {{Main|Economy of Oportia}} | ||
Following the [[Oportian special national referendum, 1722|1722 referendum]], Oportia adopted significant economic reforms, including a national progressive taxation system and employment programs in government infrastructure and community projects. The economy, while still heavily reliant on raw materials, is diversifying in manufacturing and services. | Following the [[Oportian special national referendum, 1722|1722 referendum]], Oportia adopted significant economic reforms, including a national progressive taxation system and employment programs in government infrastructure and community projects. The economy, while still heavily reliant on raw materials, is diversifying in manufacturing and services. | ||
===Overview=== | |||
===Energy=== | |||
===Tourism=== | |||
===Taxation and government spending=== | |||
===Alexandrium=== | |||
===Labor force=== | |||
==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
Latest revision as of 23:11, 8 November 2024
| The State of Oportia L'État d'Oportie | |||
| |||
| Motto: Official: Liberté avant tout Informal: Oportet | |||
| Anthem: Le bateau | |||
| |||
| Map versions | 17.5.7 – | ||
| Capital | Vanie | ||
| Official language(s) | Federal level: Alexandrian Istvanistani Regional level: Babkhi Pallisican Sarnechi Shahvekh Thraci | ||
| Official religion(s) | None | ||
| Demonym | Oportian | ||
| - Adjective | Oportian | ||
| Government | Constitutional federal republic under semi-direct democracy | ||
| - Federal Representative | Galilea Montijo (Liberty Now! Movement) | ||
| - Federal Chancellor | Emmanuel Aubin (Liberty Now! Movement) | ||
| - Legislature | Federal Congress of Oportia | ||
| Establishment | 1706 AN | ||
| Area | TBD km2 | ||
| Population | 7,803,733 (1716 census) 13,872,322 (1726 est.) | ||
| Currency | Mérite | ||
| Calendar | Norton Calendar | ||
| Time zone(s) | CMT+2 | ||
| Mains electricity | 230 V, 50 Hz | ||
| Driving side | Right | ||
| Track gauge | Standard (1,435 mm) | ||
| National website | gou.op | ||
| National forum | |||
| National animal | |||
| National food | |||
| National drink | |||
| National tree | Beech | ||
| Abbreviation | OPO, OP | ||
The State of Oportia (Alexandrian: L'État d'Oportie) is a constitutional federal republic in southern Eura, known for its unique system of semi-direct democracy and strong civil liberties. Founded in 1706 AN through the union of several autonomous city-states under the Compagnie Generale d'Oportia in Eura, Oportia has developed into a significant regional power, with its capital at Vanie. The nation operates under a four-branch system of government that includes the executive, legislative, judicial, and the Federal Electorate, a novel democratic institution comprising all registered voters that serves as a direct check on governmental power.
Since its establishment, Oportia has emerged as a notable example of democratic governance, ranking first in the Micras Democracy Index in 1707 AN with maximum scores in political participation and civil liberties. The country underwent significant political reform in 1722 AN following the 1721 Oportian protests, transitioning from its First Republic to the current Second Republic, which strengthened democratic institutions and established a bicameral legislature. This period also saw the implementation of major economic reforms, including the introduction of a progressive taxation system and expanded public infrastructure programs.
Oportia's political alignment has evolved substantially over time, moving from membership in the Xäiville Convention (1719 AN-1729 AN) to joining the Raspur Pact in 1729 AN. Under the leadership of Federal Representative Galilea Montijo, the country has experienced rapid economic growth, driven by the exploitation of Alexandrium deposits and aggressive export-oriented policies. The nation maintains a diverse linguistic landscape, with Alexandrian and Istvanistani as federal languages, while regional languages include Babkhi, Pallisican, Sarnechi, Shahvekh, and Thraci, reflecting its multicultural heritage and immigrant population.
History
Formation
- 1690 AN-1705 AN, Background:
- Tied to the formation of Altus and Alduria (all the way back).
- Formation of Alduria-Wechua after 1685 Aldurian coup d'etat, formation of Nouvelle Alexandrie after rapid expansion in 1693 AN
- Regional wars: Third Euran War, Operation Paramount, etc etc.
- The development of the Compagnie Generale d'Oportie by Jean Nouel. New venture copying the Aldurian venture (which grew into Nouvelle Alexandrie in less than a century) but keeping it as a republic like Alduria originally was. Led by people in Altus that were very libertarian, military-oriented, more traditional; but then came to be significantly supported by Aldurians in Natopia, which were more affluent, more giving, and more progressive. The common thread between them was liberty, profit, and orientation to the military or public/community service. Venture fragmented into a bunch of different competing ventures, with Jean Nouel's original venture almost failing entirely. This led to the foundation of several city states and individual "petty republics" with the largest of them being Vanie. Jean basically manages to bring them all back together into a federal republic when everyone's facing serious issues surviving in Eura vs. Azad Eura, the people in the Green, etc etc.
- Formation of Oportian political culture: consensus-building, compromise, direct democracy, liberty, etc. First political organizations are formed: Jean Nouel founds the Conservative Nationalist Party of Oportia, Laurent Morsi founds the Liberal Progressive Party of Oportia. Soon, in the Alexandrian tradition, divergent movements began to form with Léa Dubois founding the Green Party of Oportia, and François Delacroix founding the Worker's Unity Party of Oportia. Sophie Marchand, independent but a Humanist sympathizer, caught some fire but did not progress too far. Seen as eccentric but honest. Martha Mitchell type of lady. Later on she founds the Nationalist & Humanist Party of Oportia in 1729 AN as the Conservative Nationalist Party of Oportia splits over Oportia leaving the Xaiville Convention and joining the Raspur Pact.
- Tie in regional history, background, and development with Zeed, Constancia, and Suren Confederacy.
First Republic (1706-1722)
- 1706 AN The State of Oportia is founded. (First Republic)
- Led by Jean Nouel, the Declaration of Vanie founds and proclaims the independence of Oportia. Union of different city states each started by different settlement companies. All form together and approve a Constitution that will be ratified in a national referendum, assembly first Federal Cabinet.
- Constitution is ratified by a public vote in 1707 AN.
- First Republic (1706-1722)
- Characteristics of the first Republic: XXXXX
- Jean Nouel, first Federal Representative of Oportia, appoints Cabinet from members of his party.
- Jean dies in office from a heart attack in 1712 AN.
- Jean is succeeded by César André who completes his Jean's term and gets elected in his own right in 1714 AN
- Territorial expansions during this time, why did they happen,. how they impacted Oportia.
- (XIV.1709 AN and III.1710) Yamaqhachan insurgency.
- (22.XIV.1716) Souduraine clash.
- César André serves until the 1721 Oportian protests have him and his party removed in the Oportia emergency national referendum, 1721.
- Celine Beaumont installed as caretaker Federal Representative of Oportia., caretaker government installed until general elections in early 1722 AN
Second Republic (1722 - Now)
- The transformation into a federal republic followed a national referendum in 1722 AN, alongside the Oportian special general election. This is generally considered as the end of the First Oportian Republic and the start of the Second Oportian Republic.
- Second Republic (1722-Now)
- Celine Beaumont is elected in her own right as Federal Representative in 1722 and 1726. Rise of the Liberal Progressive Party of Oportia.
- Oportian economic crisis, Oportia joins the Euran Economic Union, gets rescue package from the EEU and Natopia.
- Oportian economic recovery, territorial expansion, continued reforms, Oportian Defense Review 1723, political and domestic events, etc.
- Oportia leaves the Xaiville Convention and joins the Raspur Pact.
- 1730 general elections: Celine Beaumont is ineligible to run for re-election a third time due to the limitations of the Oportian Constitution.
Geography
Government and politics
The State of Oportia operates as a constitutional republic under a system of representative democracy that incorporates elements of direct democracy through the Federal Electorate, a unique fourth branch of government. This structure allows for a balanced distribution of power among the executive, legislative, and judicial branches, while ensuring that the citizenry has a direct voice in the governance process.
Constitution
The new Constitution, established in 1722 AN as a result of the 1721 Oportian protests and subsequent reforms, balances powers between the federal and city levels. It introduced a bicameral representative legislature while keeping the Federal Electorate of Oportia, tipping the balance in favor of more representative democracy. Key aspects of the Constitution include political neutrality for a greater amount of public offices, environmentalism, and expanded human rights protections.
Executive
The Head of State is the Federal Representative, who presides over the Federal Cabinet. The Federal Chancellor of Oportia acts as the Deputy, with specific reserved powers over foreign affairs and special responsibilities.
Legislature
The Federal Congress of Oportia is the bicameral representative legislature of Oportia, divided into two chambers: the lower chamber (and most powerful), the Chamber of Deputies of Oportia, and the upper chamber, the Senate of Oportia. Federal Congress has constitutionally reserved powers that include proposing and voting on laws, political appointments, policies, and public initiatives.
Federal Electorate
The Federal Electorate of Oportia comprises all registered voters in Oportia, functioning as a fourth branch of government. This body has the power to propose legislation, call for referendums on critical issues, and directly participate in decision-making processes that affect national policy. The Federal Electorate ensures that Oportia's democracy is vibrant, participatory, and responsive to the will of the people.
Judiciary
The Federal High Court is the highest court, overseeing violations of the Constitution of Oportia and federal law.
Foreign Relations
Raspur Pact
Law enforcement and military
The Oportian Security Forces encompass civilian police services, military units, and special operations forces, maintaining internal security, defending national sovereignty, and contributing to international peacekeeping efforts. Structured to respond to a variety of challenges, the Security Forces operate under strict oversight to ensure they adhere to democratic principles and respect for civil liberties.
Economy
Following the 1722 referendum, Oportia adopted significant economic reforms, including a national progressive taxation system and employment programs in government infrastructure and community projects. The economy, while still heavily reliant on raw materials, is diversifying in manufacturing and services.
Overview
Energy
Tourism
Taxation and government spending
Alexandrium
Labor force
Demographics
As of 1726 AN, Oportia's estimated population stands at approximately 13.8 million.
Culture
At its core, Oportian society cherishes the ideals of liberty, democracy, and community, fostering an environment where entrepreneurship and innovation thrive. The national ethos places a strong emphasis on the active participation of its citizens in both the political sphere and in community life, mirroring a commitment to direct democracy and civic engagement. The culture is characterized by a profound respect for individual freedoms and rights, coupled with a collective responsibility towards environmental stewardship and social welfare. This blend of values cultivates a community-oriented mindset among Oportians, foundational to the nation's identity. Its foundations are primarily Alexandrian-influenced, with prominent Babkhi, Zeedic, Constancian, and Natopian regional influences. Since its founding in 1706 AN, its culture has been influenced by successive waves of immigrants and the resulting mix of cultures has become a distinguishing feature of its society. This has made Oportia a fusion of elegance and tradition, where the architectural and artistic influences reflect a harmonious blend of classical and contemporary styles influenced by its Euran neighbors and by its past. The urban landscapes are meticulously planned to balance the beauty of public spaces with functional design, promoting a lifestyle where walking and cycling are integral to daily life. This emphasis on sustainable living and public welfare is evident in the careful attention to public gardens, art installations, and communal areas that serve as hubs of cultural exchange and social interaction. Politically, Oportia is deeply rooted in the principles of individual liberty, direct democracy, consensus-building, and inclusivity.
Holidays
Oportia celebrates a variety of national holidays that reflect its rich cultural heritage, democratic values, and commitment to liberty and community. Major holidays include:
- Liberation Day: Commemorates the founding of the State of Oportia and its declaration of independence. It is a day of national pride, celebrated with parades, speeches, and public ceremonies.
- Democracy Day: Marks the anniversary of the first democratic elections in Oportia. Celebrations include public debates, civic education events, and community gatherings to honor the nation's democratic tradition.
- Unity Festival: A three-day festival (with one day as a national holiday) celebrating the diverse cultural backgrounds of Oportia's citizens. Festivities involve traditional music, dance, food fairs, and exhibitions showcasing the rich tapestry of Oportian society.
- Constitution Day: Observes the ratification of the Oportian Constitution. Government buildings are open to the public, and educational programs are held to foster understanding of the constitutional principles and rights. This day also commemorates the 1721 Oportian protests, leading to significant reforms and the adoption of the Constitution.
- Innovation Day: Recognizes Oportia's commitment to education, self-improvement, technological advancement, and innovation. Events include science fairs, startup expos, and workshops aimed at inspiring the next generation of educators, scientists, and innovators.
- Liberty Day: Dedicated to promoting liberty, tolerance, and mutual respect among all Oportians. Activities focus on community service, dialogue, charitable donations, and acts of kindness, reinforcing the values of unity and cooperation.
- Christmas' Eve & Christmas Day: Celebrated with family gatherings, religious services, and communal festivities, reflecting the universal spirit of goodwill, peace, and joy.
- New Year's Eve & New Year's Day: Mark the conclusion of the old year and the beginning of the new. Celebrations include fireworks, parties, and reflections on the year past and the year ahead, embodying hopes for prosperity, peace, and progress.
Media
Music
Cuisine
See also
- Vanie, the capital and largest city of Oportia;
- History of Oportia;
- Government and politics of Oportia;
- Oportian Security Forces;
- Constitution of Oportia;
- Laws of Oportia;
- Economy of Oportia.

