Oportia
| The State of Oportia L'État d'Oportie | |||
| |||
| Motto: Liberté avant tout | |||
| Anthem: Le bateau | |||
| |||
| Map versions | 17.5.7 – | ||
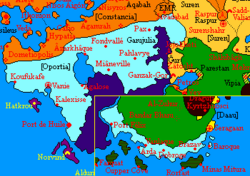
| Capital | Vanie | ||
| Official language(s) | Federal level: Alexandrian Istvanistani Regional level: Babkhi Pallisican Sarnechi Shahvekh Thraci | ||
| Official religion(s) | None | ||
| Demonym | Oportian | ||
| - Adjective | Oportian | ||
| Government | Constitutional federal republic under semi-direct democracy | ||
| - Federal Representative | Céline Beaumont | ||
| - Federal Chancellor | Felipe de Borbón y de los Santos | ||
| - Legislature | Federal Congress of Oportia | ||
| Establishment | 1706 AN | ||
| Area | TBD km2 | ||
| Population | 7,803,733 (1716 census) 13,872,322 (1726 est.) | ||
| Currency | Mérite | ||
| Calendar | Norton Calendar | ||
| Time zone(s) | CMT+2 | ||
| Mains electricity | 230 V, 50 Hz | ||
| Driving side | Right | ||
| Track gauge | Standard (1,435 mm) | ||
| National website | gou.op | ||
| National forum | |||
| National animal | |||
| National food | |||
| National drink | |||
| National tree | Beech | ||
| Abbreviation | OPO, OP | ||
The State of Oportia (Alexandrian: L'État d'Oportie) is a country located in the south of continent of Eura.
In 1707 AN, the country was ranked first in Micras Democracy Index, with maximum score in political participation and civil liberties. In 1719 AN, the country accessed the Xäiville Convention, a non-aligned political organisation of democratic states.
Etymology
Oportia's name comes from Alexandrian words "eau" (pronounced o, meaning water) and "port".
History
Government
Executive
The Head of State and Government is the Federal Representative, who presides over the Federal Cabinet and all its ministries.
Legislature
The Federal Electorate is the legislative body of Oportia and is comprised of the national electorate, which proposes and votes on laws, public initiatives and referendums, and the Federal Representative, whose task is approving or rejecting the passed motions.
Judiciary
The Federal Court is the supreme court in Oportia, and has jurisdiction over violations of constitution and constitutional rights, federal law, inter-administrative laws and international laws the nation has been obliged to abide.
Politics
Constitution
Oportian Constitution defines basic and political rights of individuals, as well as dividing power, jurisdiction and authority between the federal and city level.
Some of the most important laws in the Constitution are:
- Political and military neutrality of the state
- Prohibition of taxes
- Freedom of navigation of all commercial ships, regardless of their origin
- Freedom of import and export of legal goods, regardless of their origin
- Prohibition of death penalty
- Gun ownership rights
- Tendency towards environmentalism
Law enforcement and military
Unlike other countries, the law enforcement and territorial defense of Oportia is the responsibility of a single centralized government body, the Security Forces, which is divided into three component commands: Civilian Command, Military Command, and Special Command.
Economy
Oportia is a market economy. Since Oportia is a state with no taxes and only basic regulations, businesses and workers enjoy wide economic freedom and prosperity in all economic sectors. Workers' rights are protected by Constitution. The private sector is dominating in all economic spheres. Public sector has a notable presence in the country's economy, and its purpose is creating profit for the funding of the state activities. The extraction and production of raw materials is the most important sector of the Oportian economy, with manufacturing and service sectors growing since the country's independence.

