Federal Assembly of Nouvelle Alexandrie
| Federal Assembly of Nouvelle Alexandrie Hukllachasqa Huñunakuy Wechua | |
| 4th Cortes Federales | |
| File:SealFederalAssembly.png Seal of the Federal Assembly of Nouvelle Alexandrie | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1693 AN |
| Preceded by | Federal Constituent Assembly (1685 AN-1693 AN) |
| Leadership | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 638 deputies |
 | |
Political groups |
|
| Meeting place | |
The Federal Assembly (Alexandrian: Asamblea Federal) is the lower house of the Cortes Federales, Nouvelle Alexandrie's legislative branch. The Assembly meets in the Legislative Palace in Cárdenas.
It has 638 elected members that are chosen from each of the regions through proportional representation using the Sainte-Laguë method. Deputies serve four-year terms. The presiding officer is the Speaker of the Federal Assembly, who is elected by the members thereof.
In the Assembly, MPs from political parties, or groups of parties, form parliamentary groups. Groups must be formed by at least 10 deputies, but a group can also be formed with only 3 deputies if the parties got at least 5% of the nationwide vote, or 15% of the votes in the regions in which they ran. The deputies who do not belong to parties form their own parliamentary group called the Independents.
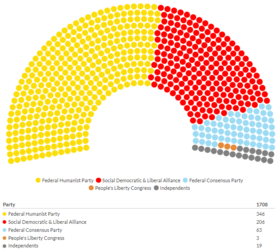
After the New Alexandrian general election, 1708, the Federal Humanist Party has absolute majority of the Assembly and therefore forms the Government party.
Constitutional position
House's nature
Composition
Article 7 of the Proclamation of Punta Santiago establishes that political parties shall be democratic, open, and lawful, and can only be disbanded or rejected by the High Court of Justice. Furthermore, Chapter IV establishes that the Assembly is composed of all of the Deputies elected from each of the Regions by proportional representation. At present, the Assembly has 637 Deputies, as agreed by the parties under the Cortes Federales Act.
Electoral system
The Proclamation establishes that Deputies are chosen by Universal, free, equal, direct, and secret sufrage. The election period is every four years, except in the case of a snap elections. The members of the Congress are elected by proportional representation with Open List and a Region-by-Region system. Seats are apportioned to each region using the Sainte-Laguë method. There is a seat threshold of 2% of the votes per region. The voting age is 18 years.
Mandate
The deputies' term of office finishes four years after their election, or when the Cortes is dissolved. The dissolution's rights belongs to the Monarch who exercises it by request of the President of the Government after the deliberation of the Council of State and under its sole responsibility. The dissolution of the Cortes also takes place if there is a failed legislature or two months after a feiled investiture session, in which case the Monarch dissolves the Assembly with the countersign of the Speaker of the Federal Assembly. During their mandate, the deputies have some guarantees and privileges to carry their responsibilities out according to Article 31 of the P{roclamation.
Bodies of the Assembly
Exercising the autonomy recognised by the Proclamation to the Assembly, the house is regulated by some internal rules established by itself in 1693 AN and it configures different government bodies to carry the pertinent competencies out.
Governing bodies
The governing bodies of the Federal Assembly are the bodies which under their authority the House is manage. Those bodies are the Speaker, the Presidium and the Board of Spokespersons.
The Speaker of the Federal Assembly is the highest authority and it represents the House and it is, de facto, the whole parliament leader. As head of the Assembly, it also chairs the Presidium, the Board of Spokespersons and the Permanent Deputation, and is the maximum responsible authority of the Congress' Police.
The Presidium of the Federal Assembly is the collective body that represents the House and manages the day-to-day of the Chamber, preparing the budget and making all the necessary decisions to allow the proper functioning of the functions of the Assembly.
The Board of Spokespersons of the Federal Assembly is the collective body formed by representatives of the parliamentary groups and normally, government representatives, that establishes the agenda of the House.
Working bodies
The working bodies of the Federal Assembly are the Plenary, the Committees, the Permanent Deputation and the Parliamentary Groups.
The Plenary is the central body of the Federal Assembly which allows the house for exercising their choices. It is the reunion of all the members of the Parliament when half plus one of its members are attending the house. This body represents the unity of the house and it works through the plenary sessions which can be ordinary or extraordinary.
The Committees are the basic working bodies of the Assembly. They are composed of a proportional number of deputies depending on the numerical importance of the parliamentary groups of the house. The committees are classified as follows: permanent or non-permanent and legislative or non-legislative.
The permanent legislative committees examine and rule the projects and bills. The Plenary of the Assembly can confer them full legislative power in relation to a matter, so they can permanently approve or reject any project or bill. The regulations of the Assembly establish 20 permanent legislative committees. The permanent non-legislative committees have responsibilities not related to the legislative production. The regulations of the Assembly establish 6 permanent non-legislative committees, and they allow the Plenary to create another ones at the beginning of each legislature. The non-permanent committees are created with a specific purpose and their themes and duration are beforehand determined by the Plenary of the Congress.
The Permanent Deputation is a body created in order to have a permanent constituted legislative power. It is responsible for safeguarding the powers of the house between the legislative sessions (when it is in Recess) or when their term has finished because of termination or dissolution. In these three cases, the Permanent Deputation is a temporary extension of the house. The Permanent Deputation is presided by the Speaker of the Federal Assembly. It is composed of a proportional number of deputies depending on the numerical importance of the different Parliamentary Groups.
The Parliamentary Groups are groups of members of the house which join together depending on their ideology. The Rules of the Cortes establish that 10 deputies at least are needed to make a parliamentary group. However, they can make a group if they are at least 3 deputies and they have got at least 15% of the total votes of the region where they have run at or 5% of the total votes of the country. The formation of the parliamentary groups takes place at the beginning of each legislature. The deputies who do not enrol in any parliamentary group constitute the Independents.
Composition of the 4th Legislature
See also: 4th Cortes Federales and New Alexandrian general election, 1708
The 4th legislature of Nouvelle Alexandrie started in 1708 AN when the Cortes Federales were constituted, once the New Alexandrian general election, 1708 was held.
Presidium of the Federal Assembly
| Position | Holder | Party |
|---|---|---|
| Speaker | George Henderson | Independent |
| 1st Deputy Speaker | Jose Angel Ferrer | FHP |
| 2nd Deputy Speaker | Abril Obrero | FHP |
| 3rd Deputy Speaker | Carmen María Laguna | SDLA |
| 4th Deputy Speaker | Cloe Ballesteros | FHP |
| First Secretary | Augustin Soria | N/A |
| Second Secretary | Mateo Pandero | |
| Third Secretary | Alberto Linares | |
| Fourth Secretary | Yolanda Sabater |
Committees
The Federal Assembly creates at the beginning of each meeting a series of committees and subcommittees. These bodies purpose is to facilitate the work of the house. The committees have the same powers as the House' Plenary: to control the government by requesting information to the Administration or by requesting the appearance of any member of the Government or Administration; and to legislate by delegation of the plenary and at the request of the Assembly's Presidium. The committees also debate the bills originated at the Plenary and the possible amends.
According to the Nouvelle Alexandrie parliamentary system, in the Congress there are two type or subcommittees, the ordinary subcommittees which purpose is to discuss and make a report about a specific issue and the reporting subcommittees which purpose is to write a first bill proposal to be discussed in the committee.
The committees can be standing committees, which creation is mandatory by the Assembly's standing rules or other laws or non-standing committees, which are created by the Plenary. The subcommittees are also created by the Plenary at the request of the committees.
The members of the committees are designated by the parliamentary groups, and once the committees are created they must elect in their first meeting the 'Bureau of the Committee', composed by a chair, two deputy chairs and two secretaries. The members of the subcommittees are designated by the committee.
Current Committees (4th legislature, 1708 AN-Present)
Permanent Legislative Committees
| Committee | Current # of Members | Term |
|---|---|---|
| Constitutional Affairs | 46 | 1706 AN-present |
| Foreign Affairs | 38 | 1708 AN-present |
| Justice | 38 | 1708 AN-present |
| Defence | 38 | 1708 AN-present |
| Finance | 38 | 1708 AN-present |
| Budget | 42 | 1706 AN-present |
| The Interior | 38 | 1708 AN-present |
| Healthcare and Social Care | 38 | 1706 AN-present |
| Civil Works and Transport | 34 | 1708 AN-present |
| Housing, Rural Affairs, and Local Government | 34 | 1708 AN-present |
| Energy, Environment, and Business Strategy | 34 | 1708 AN-present |
| Education | 34 | 1708 AN-present |
| Labor, Social Security, and Pensions | 30 | 1708 AN-present |
| Industry, Trade and Tourism | 30 | 1708 AN-present |
| Human, Civil and Social Rights | 24 | 1708 AN-present |
| Agriculture, Fisheries and Food | 24 | 1708 AN-present |
| Science, Technology, and Innovation | 24 | 1708 AN-present |
| Culture and Sports | 24 | 1708 AN-present |
| Economic Affairs, Communications, and Media | 24 | 1706 AN-present |
| International Cooperation and Development | 18 | 1706 AN-present |
Permanent Non-Legislative Committees
| Committee | # of Members | Term |
|---|---|---|
| Rules and Regulations | 18 | 1706 AN-present |
| Petitions | 12 | 1706 AN-present |
| Appointments | 14 | 1706 AN-present |
| Democratic Quality, Anti-Corruption, and Institutional and Legal Reform | 18 | 1706 AN-present |
| Children and Adolescents' Rights | 8 | 1706 AN-present |
| Palace Affairs | 8 | 1706 AN-present |
