Confederate States of Floria Congress

The Confederate States of Floria Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of Floria, and consists of two chambers: The House of Representatives and the Florian Senate. The congress is located in the Confederate States of Floria Capitol in Northcliff, Kingsland.Members of Congress are elected by direct vote though some members of the Seante are appointed by State governors.Congress has a total of 130 voting members which includes 30 senators and 100 representatives. The vice president of the Confederate States, as President of the Senate, has a vote in the Senate only when there is a tie.
The members of Congress serve 12 AN year terms representing the people of a single constituency, known as a "district". "Districts" are determined by population using up to date census results and each state must have at least one representative. The Congress was created after the constitutional change in early 1680 replacing the former parliamentary system which had existed since the formation of the country. Congress members are typically affiliated with two major parties, the UPR or the Social Democratic Party of Floria.
The Florian Congress is the bicameral legislative branch of the government of Floria, responsible for making laws, overseeing the government, and representing the interests of the Florian people. It consists of two chambers: the House of Representatives and the Senate.
House of Representatives
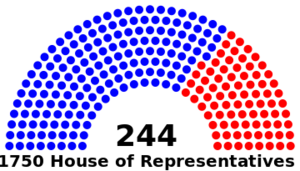
The House of Representatives comprises 244 seats, elected by the people of each state based on population and geographical representation. It holds considerable authority over fiscal matters, including passing laws, approving budgets, and scrutinising executive actions.
Representation in the House is determined by the population of each state, with more populous states having a larger number of representatives. For instance, Southland, one of the most populous states, has 40 representatives, while smaller states like the Temple Islands have only 4. Representatives serve a 12-year term.
Senate
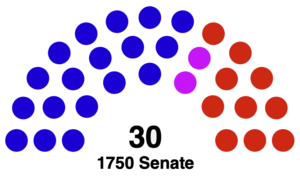
The Senate, the upper chamber of the Florian Congress, comprises 30 seats. Each state is represented by two senators, ensuring equitable representation for all states irrespective of population. Senators serve six-year terms, with one-third of the Senate being elected every two years.
The Senate’s primary responsibilities include reviewing and amending legislation passed by the House, approving presidential appointments, ratifying treaties, and assuming a pivotal role in national security and foreign policy decisions.
As of the current political configuration, the Senate is controlled by a United Republican coalition, in alliance with the Party of Justice & Harmony, which holds 18 seats. This majority grants the United Republicans substantial influence over the legislative agenda.
Congressional Leadership
Leadership within the Congress is divided between the two chambers. In the House of Representatives, the Speaker of the House is elected by the representatives and presides over debates, sets the legislative agenda, and ensures the passage of bills.
In the Senate, the Senate Majority Leader, elected by the majority party, leads the legislative process, helps shape policy, and plays a pivotal role in confirming presidential appointments and ratifying treaties.
Committees
Both the House and Senate have committees dedicated to specific areas of legislation. These committees review proposed bills, hold hearings, and make recommendations on whether to advance a bill to the full chamber for a vote. Committees handle diverse topics, such as defense, healthcare, and education.
Electoral Influence
The members of Congress are directly elected by the people, which allows the legislative branch to be responsive to public opinion and political shifts. The balance of power in Congress can change with each election, influencing the legislative process.
Relationship with Executive and Judicial Branche
While Congress holds the power to create laws, the executive branch, led by the president, enforces them. The judicial branch, headed by the Supreme Court, interprets laws and ensures they are in line with the Constitution.