Badia: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
OlegnalehciM (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
|leader_title= | |leader_title= | ||
|leader_name= | |leader_name= | ||
|area_total_km2= | |area_total_km2=72416.16 | ||
|population_total={{get parameter|dataBadia|VEGcityPOP|Template:VEGcityPOP/doc}} | |population_total={{formatnum:{{get parameter|dataBadia|VEGcityPOP|Template:VEGcityPOP/doc}}}} | ||
|population_as_of={{VEGcensus}} | |population_as_of={{VEGcensus}} | ||
|population_density_km2= | |population_density_km2=auto | ||
|population_demonym=Badiese | |population_demonym=Badiese | ||
|timezone1= CMT+2 | |timezone1= CMT+2 | ||
|footnotes=}}'''Badia''' (/'badˈia/), in [[Istvanistani]] sometimes referred to as ''Abbey'', is a region of [[Vegno]], located in the north-west section of the country, bordering the regions of [[Pelago]] and [[Buonriposo]] to the east, [[Ponente]] to the south, and the nation of [[Lac Glacei]] to the west; it overlooks also, for 180 kms, into the [[Northern Sea]]. The region comprises a population of about {{get parameter|dataBadia|VEGcityPOP|Template:VEGcityPOP/doc}} inhabitants. | |footnotes=}}'''Badia''' (/'badˈia/), in [[Istvanistani]] sometimes referred to as ''Abbey'', is a region of [[Vegno]], located in the north-west section of the country, bordering the regions of [[Pelago]] and [[Buonriposo]] to the east, [[Ponente]] to the south, and the nation of [[Lac Glacei]] to the west; it overlooks also, for 180 kms, into the [[Northern Sea]]. The region comprises a population of about {{formatnum:{{get parameter|dataBadia|VEGcityPOP|Template:VEGcityPOP/doc}}}} inhabitants (on {{VEGcensus}}). | ||
Its chief town and largest city is [[Lamino]]. | Its chief town and largest city is [[Lamino]]. | ||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
! style="background:#ccf;" |Area (km<sup>2</sup>) | ! style="background:#ccf;" |Area (km<sup>2</sup>) | ||
! style="background:#ccf;" |Population | ! style="background:#ccf;" |Population | ||
! style="background:#ccf;" |Density | <small>({{VEGcensus}} census)</small> | ||
! style="background:#ccf;" | Density | |||
(inhabitants/km<sup>2</sup>) | (inhabitants/km<sup>2</sup>) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Lamino]] | |[[Lamino]] | ||
| | |20,093.76 | ||
|{{Get parameter|dataLamino(LA)|VEGcityPOP|Template:VEGcityPOP/doc}} | |{{formatnum:{{Get parameter|dataLamino(LA)|VEGcityPOP|Template:VEGcityPOP/doc}}}} | ||
| | |{{formatnum:{{Round|{{#expr:({{get parameter|dataLamino(LA)|VEGcityPOP|Template:VEGcityPOP/doc}}/20093.76)}}|2}}}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Motta Follonica]] | |[[Motta Follonica]] | ||
| | |15,256.8 | ||
|{{Get parameter|dataMotta Follonica(MF)|VEGcityPOP|Template:VEGcityPOP/doc}} | |{{formatnum:{{Get parameter|dataMotta Follonica(MF)|VEGcityPOP|Template:VEGcityPOP/doc}}}} | ||
| | |{{formatnum:{{Round|{{#expr:({{get parameter|dataMotta Follonica(MF)|VEGcityPOP|Template:VEGcityPOP/doc}}/15256.8)}}|2}}}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Sassomasso]] | |[[Sassomasso]] | ||
| | |17,040.96 | ||
|{{Get parameter|dataSassomasso(SS)|VEGcityPOP|Template:VEGcityPOP/doc}} | |{{formatnum:{{Get parameter|dataSassomasso(SS)|VEGcityPOP|Template:VEGcityPOP/doc}}}} | ||
| | |{{formatnum:{{Round|{{#expr:({{get parameter|dataSassomasso(SS)|VEGcityPOP|Template:VEGcityPOP/doc}}/17040.96)}}|2}}}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Villamagna Marittima]] | |[[Villamagna Marittima]] | ||
| | |20,024.64 | ||
|{{Get parameter|dataVillamagna Marittima(VM)|VEGcityPOP|Template:VEGcityPOP/doc}} | |{{formatnum:{{Get parameter|dataVillamagna Marittima(VM)|VEGcityPOP|Template:VEGcityPOP/doc}}}} | ||
| | |{{formatnum:{{Round|{{#expr:({{get parameter|dataVillamagna Marittima(VM)|VEGcityPOP|Template:VEGcityPOP/doc}}/20024.64)}}|2}}}} | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 23:45, 29 September 2023
| Badia | |
|---|---|
| Region of |
|
 |
|
| Capital | Lamino |
| Area | |
| • Total | 72,416.16 km2 (27,960.04 sq mi) |
| Population (1747 AN) | |
| • Total | 357,533 |
| • Density | 4.9/km2 (13/sq mi) |
| Demonym | Badiese |
| Time zone | CMT+2 |
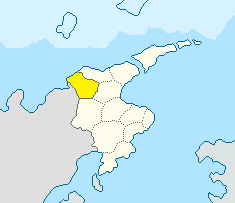
Badia (/'badˈia/), in Istvanistani sometimes referred to as Abbey, is a region of Vegno, located in the north-west section of the country, bordering the regions of Pelago and Buonriposo to the east, Ponente to the south, and the nation of Lac Glacei to the west; it overlooks also, for 180 kms, into the Northern Sea. The region comprises a population of about 357,533 inhabitants (on 1747 AN).
Its chief town and largest city is Lamino.
Geography and climate
The Badia Region is characterized by a great variety of natural landscapes. To the north extends a vast plain which, before overlooking the North Sea, becomes mountainous again, to create a large coastal cliff, within the province of Villamagna Marittima. To the south-east, however, some majestic mountains rise accompanied by hills that are easily habitable and cultivable.
The climate in Badia is Nordic, with harsh winters and cool summers. Average winter temperatures usually fall below freezing, while in summer they hover around 15°C. Furthermore, the region, like the others in the northern area of Vegno, is often covered by a thick layer of winter snow, creating enchanting views, very attractive for tourists.
History
As regards recent history, Badia was initially under the rule of the Republic of Freeland, after the fall of which the region experienced a period of nomadism, during which the population sought a new identity and the opportunity to live without a government central. This tumultuous period, however, culminated with the annexation referendum of 1707 to the nation of Vegno, with an overwhelming victory for the "Yes". From that moment, Badia was annexed and became a fundamental part of Vegno, contributing to its rich cultural diversity.
Economy
The Badia Region, located in a privileged position along the north coast of Vegno, presents a diversified economy with a long tradition linked to the primary sector and a growing emphasis on the tertiary sector.

Fishing has long been the pillar of Badia's economy. Nutrient-rich coastal waters have made sustainable fishing of several fish species possible, with a particular emphasis on catching salmon and tuna. These activities have historically represented the main source of income for the local community, with expert fishermen operating both in small traditional boats and in modern industrial fleets. However, to ensure the sustainability of marine resources, stringent regulations and control measures have been introduced to avoid overexploitation.
Agriculture is another significant aspect of Badia's primary sector. The temperate summer climate conditions of the region favor the cultivation of a wide range of agricultural products. Local farmers have committed to using sustainable agricultural practices, including crop rotation and responsible use of fertilizers. Major agricultural products include grains such as wheat and oats, vegetables such as tomatoes and carrots, and fruits such as apples and pears. However, the use of greenhouses during the winter is very widespread, given the very cold temperatures of the colder season. Agriculture contributes significantly to the region's food security.
In recent years, tourism has emerged as a growing sector in Badia's economy. The capital city, Lamino, with its historic architecture, museums and vibrant cultural scene, has become a very popular tourist destination. The coastal region, with pristine beaches and natural cliffs in the province of Villamagna Marittima, attracts tourists from all over the world. The tourism industry has brought increased income and employment opportunities for the local community. Numerous hotel facilities, high-quality restaurants and souvenir shops have been built to meet the needs of visitors.
The tertiary sector also includes retail and services. Lamino is a major shopping centre, with a variety of shops offering high quality products. Local shops and markets are meeting places for the community, and small businesses and independent traders thrive, contributing to the economic vitality of the region. In addition to physical stores, online commerce is gaining popularity, allowing local businesses to expand their customer base.
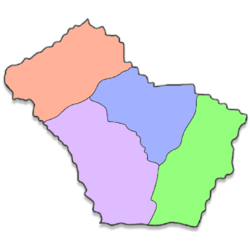
Administrative divisions
Badia is divided into five provinces and one metropolitan city:
| Province | Area (km2) | Population
(1747 AN census) |
Density
(inhabitants/km2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lamino | 20,093.76 | 152,451 | 7.59 |
| Motta Follonica | 15,256.8 | 68,431 | 4.49 |
| Sassomasso | 17,040.96 | 74,545 | 4.37 |
| Villamagna Marittima | 20,024.64 | 62,103 | 3.10 |
Cuisine
The cuisine of the Badia region is characterized above all by typical Nordic sea flavors, characterized by the freshness of the fish, in particular salmon and tuna, and by the abundant use of local vegetables. This coastal region offers a rich culinary tradition that has developed thanks to its privileged location along the crystal clear waters of the Northern Sea.

Local dishes include the typical Badiano Salmon with Blueberry Sauce: the fresh salmon is delicately grilled and served with a sauce made from local blueberries, which adds a fruity and acidic note to the succulent flesh of the fish. In addition to this, the Badia Tuna with Seaweed Salad: in which the fresh tuna is marinated with aromatic herbs and then lightly seared to preserve its softness. It is then served with a salad of seaweed harvested from the coast, enriched with a vinaigrette made from local olive oil.
Even the former, however, are preponderant such as Badia's seafood tagliatelle which is a dish loved in this region by both residents and tourists and consists of fresh tagliatelle seasoned with a rich sauce based on seafood, including shrimp , mussels and clams, all cooked in an aromatic fish broth.
Local vegetables grown on the plains and hills of the region, including cabbage, carrots, turnips and potatoes, are often served as side dishes or used to enhance main dishes. For example, fresh salad with lemon dressing is a common accompaniment for many dishes.
As for drinks, dry white wine, produced from local vineyards, is often served with meals. However, craft beer is just as popular, with a range of local breweries producing unique beers that pair perfectly with the local cuisine. Traditional desserts include fresh fruit pies, seafood-flavored ice cream and chocolate cakes with hints of sea salt. Often, these delights are prepared with local ingredients to ensure an authentic dining experience.
Infrastructure and Transport

The Badia region, located along the Nordic coast, is equipped with an infrastructure and transport system that promotes connectivity and mobility for both residents and visitors. These infrastructures play a crucial role in facilitating travel within the region itself and to surrounding areas.
The A4 Autostrada is the main land connection in the Badia region. This modern highway crosses the entire region, connecting its capital, Lamino, to all the local provinces. Towards the south, the A4 highway extends to Scanzata, providing quick access to Vegno's inland towns and villages. Heading north, the highway continues to Agropl, ensuring a direct connection with the northern and eastern areas of the nation. This road network is essential for the transport of goods and people.
The Badia region is also served by a well-developed railway network. The Santa Maria di Lamino station represents the main railway hub in the region. This strategically located station is a departure and arrival point for numerous regional and national trains, connecting the region to surrounding cities and towns. The rail system offers a convenient and environmentally sustainable alternative to the use of the car for travel within the region and to external destinations.
Within the Badia region, a local public transport service is available that connects smaller towns and communities. These services include a network of buses and trams providing an accessible option for daily travel within the region. This system is essential for local transportation and connecting people to the services and opportunities offered by the region. Furthermore, the national company Linard Trasporti also organizes buses and lines with national connections.