T-7/A-6 Víbora: Difference between revisions
Continuator (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Continuator (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
| data4 = {{AN|1724}} | | data4 = {{AN|1724}} | ||
| label5 = Number built | | label5 = Number built | ||
| data5 = | | data5 = 439 ({{AN|1730}}) | ||
| label6 = Designed | | label6 = Designed | ||
| data6 = {{AN|1718}} – {{AN|1723}} | | data6 = {{AN|1718}} – {{AN|1723}} | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
Begun in {{AN|1718}} as a private initiative by the aerospace arm of [[ESB Susa]], the {{PAGENAME}} was envisaged as a prospective replacement for the rapidly aging [[T-4/A-4 Flecha]], and the downright ancient [[T-2/A-2 Saeqeh]], in the inventories of [[Raspur Pact]] air forces where the combination of a rugged air trainer and versatile light attack aircraft remained a mainstay of many air arms. | Begun in {{AN|1718}} as a private initiative by the aerospace arm of [[ESB Susa]], the {{PAGENAME}} was envisaged as a prospective replacement for the rapidly aging [[T-4/A-4 Flecha]], and the downright ancient [[T-2/A-2 Saeqeh]], in the inventories of [[Raspur Pact]] air forces where the combination of a rugged air trainer and versatile light attack aircraft remained a mainstay of many air arms. | ||
The T-6/A-6 Víbora's enhanced design and capabilities have positioned it as a potential benchmark in the realm of training and light attack aircraft. Promotional materials produced by ESB Susa have been quick to assert that the story of the aircraft's development is one of innovation, adaptability, and a testament to the relentless pursuit of excellence in aviation technology. As it undergoes rigorous testing and evaluation, the aviation industry will be interested to see whether the Víbora is a worthy successor to the Flecha. | |||
=== Design and Characteristics === | |||
[[File:T-6-A-6 Víbora.png|thumb|right|Depiction of the T-6/A-6 Víbora]] | |||
The T-6/A-6 Víbora boasts a plethora of design features and characteristics that set it apart as a versatile training and light attack aircraft. Its development, undertaken by the aerospace division of ESB Susa, has yielded an aircraft that is poised to redefine the standards of aerial versatility and performance. | |||
=== Physical Attributes === | |||
The T-6/A-6 Víbora exhibits a robust yet sleek design, measuring approximately 13.8 metres in length and boasting a wingspan of 13.38 metres. Its loaded weight of 10,085 kilograms underscores its robust construction, making it well-suited for both training and combat missions. This combination of size and weight provides the aircraft with stability and agility, crucial attributes for its multifaceted role. | |||
=== Impressive Performance === | |||
In the realm of aerial performance, the T-6/A-6 Víbora does not disappoint. With a maximum speed of 763 kilometres per hour, it can swiftly respond to evolving tactical scenarios. Its combat range extends to 550 kilometres, ensuring that it can operate effectively in various theater environments. Moreover, the aircraft boasts an impressive ferry range of 2,060 kilometres, making it suitable for long-distance deployments. | |||
The T-6/A-6 Víbora's service ceiling reaches a remarkable altitude of 11,400 metres, enabling it to excel in both high-altitude reconnaissance and combat roles. Its rate of climb, at 18 metres per second, allows for swift ascents, a crucial capability in evasive maneuvers and close air support missions. | |||
=== Armaments === | |||
One of the defining features of the T-6/A-6 Víbora is its formidable armament package. The aircraft is equipped with eight wing-mounted M1693 medium machine guns, each with an impressive calibre of 8 mm RP. This firepower ensures air superiority against helicopters, hostile light aircraft, and UAVs, and enhances its effectiveness in light attack missions. | |||
In addition to its wing-mounted machine guns, the T-6/A-6 Víbora boasts four under-wing hardpoints, each with a capacity of 250 kilograms. This configuration provides the aircraft with a total combat payload capacity of 1,000 kilograms. These hardpoints enable the mounting of a diverse array of munitions, including air-to-ground missiles, bombs, and rocket pods, further expanding its versatility on the battlefield. | |||
==Timeline== | ==Timeline== | ||
| Line 62: | Line 85: | ||
**2x development prototypes; | **2x development prototypes; | ||
**1x production prototype. | **1x production prototype. | ||
*{{Team flag|Normark|name=Nordhær}} | |||
**72x ordered and delivered. 67x airworthy as of {{AN|1730}}. | |||
*{{Team flag|Nouvelle Alexandrie|name=Federal Air Force of Nouvelle Alexandrie}}: | *{{Team flag|Nouvelle Alexandrie|name=Federal Air Force of Nouvelle Alexandrie}}: | ||
**3x evaluation prototypes. | **3x evaluation prototypes. | ||
**600 ordered, {{AN|1727}}. | |||
*{{Team flag|Constancia|name=Imperial Constancian Air Force}}: | |||
**600 ordered, {{AN|1727}}. | |||
*{{Team flag|Benacian Union|name=Benacian Union Defence Force}} | |||
**600 ordered, I.{{AN|1731}} | |||
==Comparable aircraft== | |||
*{{Team flag|Babkha|name=T-2/A-2 Saeqeh}} | |||
*{{Team flag|Nouvelle Alexandrie|T-4/A-4 Flecha|name=T-4/A-4 Flecha}} | |||
*{{Team flag|Shireroth|name=IE-7 Songbird}} / [[IE-9 Extended Songbird]] | |||
[[Category: Military aviation]] | [[Category: Military aviation]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:13, 30 March 2024
 Depiction of the T-7/A-6 Víbora | |
| Type | Training and Light Attack Aircraft |
|---|---|
| Place of origin |
|
| Introduced | 1724 AN |
| Number built | 439 (1730 AN) |
| Designed | 1718 AN – 1723 AN |
| Manufacturer |
|
| Crew | 2 |
| Length | 13.8 m |
| Wingspan | 13.38 m |
| Loaded weight | 10,085 kg |
| Maximum speed | 763 km |
| Combat range | 550 km |
| Ferry range | 2,060 km |
| Service ceiling | 11,400 m |
| Rate of climb | 18 m/s |
| Armaments |
|
The T-7/A-6 Víbora, a training and light attack aircraft proposed for the air forces of Nouvelle Alexandrie and the Raspur Pact.
Development
Begun in 1718 AN as a private initiative by the aerospace arm of ESB Susa, the T-7/A-6 Víbora was envisaged as a prospective replacement for the rapidly aging T-4/A-4 Flecha, and the downright ancient T-2/A-2 Saeqeh, in the inventories of Raspur Pact air forces where the combination of a rugged air trainer and versatile light attack aircraft remained a mainstay of many air arms.
The T-6/A-6 Víbora's enhanced design and capabilities have positioned it as a potential benchmark in the realm of training and light attack aircraft. Promotional materials produced by ESB Susa have been quick to assert that the story of the aircraft's development is one of innovation, adaptability, and a testament to the relentless pursuit of excellence in aviation technology. As it undergoes rigorous testing and evaluation, the aviation industry will be interested to see whether the Víbora is a worthy successor to the Flecha.
Design and Characteristics
The T-6/A-6 Víbora boasts a plethora of design features and characteristics that set it apart as a versatile training and light attack aircraft. Its development, undertaken by the aerospace division of ESB Susa, has yielded an aircraft that is poised to redefine the standards of aerial versatility and performance.
Physical Attributes
The T-6/A-6 Víbora exhibits a robust yet sleek design, measuring approximately 13.8 metres in length and boasting a wingspan of 13.38 metres. Its loaded weight of 10,085 kilograms underscores its robust construction, making it well-suited for both training and combat missions. This combination of size and weight provides the aircraft with stability and agility, crucial attributes for its multifaceted role.
Impressive Performance
In the realm of aerial performance, the T-6/A-6 Víbora does not disappoint. With a maximum speed of 763 kilometres per hour, it can swiftly respond to evolving tactical scenarios. Its combat range extends to 550 kilometres, ensuring that it can operate effectively in various theater environments. Moreover, the aircraft boasts an impressive ferry range of 2,060 kilometres, making it suitable for long-distance deployments.
The T-6/A-6 Víbora's service ceiling reaches a remarkable altitude of 11,400 metres, enabling it to excel in both high-altitude reconnaissance and combat roles. Its rate of climb, at 18 metres per second, allows for swift ascents, a crucial capability in evasive maneuvers and close air support missions.
Armaments
One of the defining features of the T-6/A-6 Víbora is its formidable armament package. The aircraft is equipped with eight wing-mounted M1693 medium machine guns, each with an impressive calibre of 8 mm RP. This firepower ensures air superiority against helicopters, hostile light aircraft, and UAVs, and enhances its effectiveness in light attack missions.
In addition to its wing-mounted machine guns, the T-6/A-6 Víbora boasts four under-wing hardpoints, each with a capacity of 250 kilograms. This configuration provides the aircraft with a total combat payload capacity of 1,000 kilograms. These hardpoints enable the mounting of a diverse array of munitions, including air-to-ground missiles, bombs, and rocket pods, further expanding its versatility on the battlefield.
Timeline
- 12.III.1724 AN: 3x evaluation prototypes received by the Federal Air Force of Nouvelle Alexandrie. Assigned to Federal Air Training Establishment at Parap.
Operators
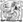 ESB Susa:
ESB Susa:
- 2x development prototypes;
- 1x production prototype.
 Nordhær
Nordhær
- 72x ordered and delivered. 67x airworthy as of 1730 AN.
 Federal Air Force of Nouvelle Alexandrie:
Federal Air Force of Nouvelle Alexandrie:
- 3x evaluation prototypes.
- 600 ordered, 1727 AN.
 Imperial Constancian Air Force:
Imperial Constancian Air Force:
- 600 ordered, 1727 AN.
 Benacian Union Defence Force
Benacian Union Defence Force
- 600 ordered, I.1731 AN
