Forajasaki

|
This article or section is a work in progress. The information below may be incomplete, outdated, or subject to change. |
| Order of the Holy Lakes in Right of the Federation of Forajasaki Perintah Tasik Suci di kanan Persekutuan Forajasaki ڤرينته تسيق سوچي دكنن ڤرسكوتوان فورجاسكي | |||
| |||
| Motto: Keadilan, Ketakwaan, Kesetiaan (Justice, Piety, Loyalty) | |||
| Anthem: Chariotic Anthem | |||
| |||
| Map versions | |||
| Capital | Kuala Forajasaki | ||
| Largest city | Kuala Forajasaki | ||
| Official language(s) | Phineaner Taesongean Eeshan | ||
| Official religion(s) | Umraism
| ||
| Demonym | Forajasakian | ||
| - Adjective | Forajasakians | ||
| Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional elective monarchy | ||
| - President (Yang Menguasai Negara) | Ahmad Abdullah Inzun Shah | ||
| - Prime Minister | Abdullah Fattah | ||
| - Legislature | Federal National Council | ||
| Establishment | |||
| Area | |||
| Population | 14,000,300 | ||
| Active population | 2 | ||
| Currency | Forajasakian ringgit, Hurmu crown | ||
| Calendar | |||
| Time zone(s) | CMT+4 and +5:20 | ||
| Mains electricity | |||
| Driving side | Left | ||
| Track gauge | |||
| National website | |||
| National forum | |||
| National animal | |||
| National food | |||
| National drink | |||
| National tree | |||
| Abbreviation | FRJ | ||
The Federation of Forajasaki (Phineaner: Persekutuan Forajasaki), officially as the Order of the Holy Lakes in Right of the Federation of Forajasaki (Phineaner: Perintah Tasik Suci di kanan Persekutuan Forajasaki), sometimes it is called Forajasaki, is one of the realm of the Order of the Holy Lakes and the member of the Confederation of the Phineonesian Nations in Western Keltia located in the Cyber-Island Chain. It is bordered by realm of Phinbella to the east and south, and the Nouvelle Alexandrie to the north through a strait.
Forajasaki is an elective monarchy formed from a federation of ten entities, namely eight states (Barbara, Sikin, Barine, Jagor, Kuala Forajasaki, Pokok Emas Islands, Tabui and Shintaro) and two autonomous regions (Bahot and Ghawur), and its capital and largest city is Kuala Forajasaki. Forajasaki is a parliamentary monarchy with a fertile democratic system. Each entity is ruled by an Emir or Sultan, the ruler of Kuala Forajasaki has been elected as the President of Forajasaki or the Head of State of Forajasaki who is called the Ruler of the State (Phineaner: Yang Menguasai Negara).
Forajasaki has over 14 million inhabitants by RP 2617. Umraism is the official religion and the Phineaner language is the official and national language of the country. The majority of the population in Forajasaki is Phineaners, while Taesongeans, Indians and Jings as well as several other ethnic groups form a minority group. Phineaners, Forajasakian Aborigines, Poyoan and Dusham are the indigenous groups of this country.
Etymology
History
- Main article: History of Forajasaki
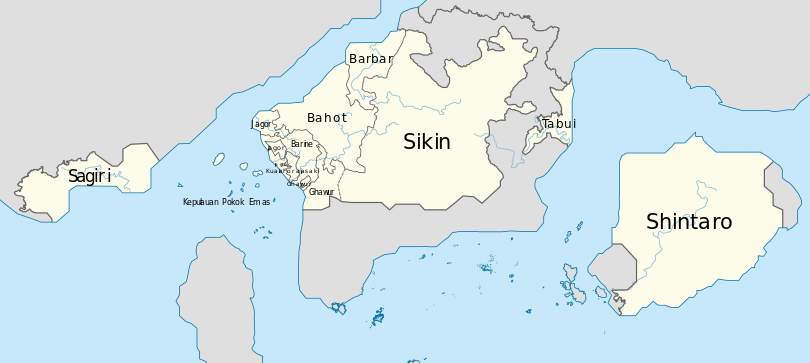
Geography
Forajasaki is located in the Cyber-Island Chain, bordered by two unnamed straits, between Phinbella and Nouvelle Alexandrie; the strait to the west of the Forajasaki area is a strategic location for the country’s and Phinbella's oil industry.
Forajasaki is located between 24°10' and 26°04' north latitude and between 64°45' and 68° east longitude. It shares a 758.27-kilometre land border with Phinbella to the south and east, and has only a water border with Nouvelle Alexandrie. The territorial boundary between Forajasaki and Phinbella may be quite resolvable even if the State of Pokok Emas Islands entity is with this boundary, and the establishment as a new state in Micras, the possibility of Forajasaki placing claims on the islands that are on the Forajasaki-Phinbella territorial waters.
The Forajasaki coast stretches for nearly 347 kilometers, most of the entities on the Forajasaki mainland are on the coast. There are several islands on the west coast of Forajasaki and on the waters border between Forajasaki and Phinbella, it includes three main islands namely Barack Island, Farahin Island and Tia Island, and the main islands as well as several small nearby islands are in one entities, of course the State of Pokok Emas Islands. Most of the small islands in the Forajasaki area are uninhabited, all of the islands are located on the west coast of Forajasaki.
Forajasaki is divided into two general regions, where to the east are high mountain ranges and narrow coastal plains in the north and make up only 72 percent of the total land area, and the other is to the west which is a lowland area with extensive coastal plains, and has river basins and make up only 28 percent of the total land area.
Biodiversity
Climate
Forajasaki tends to have a subtropical highland climate and a coastal maritime climate, and is affected by the Cyberian monsoon, with light precipitation in the summer from June to August. In the mountains and interior of the country, winters are likely to be very cold with the minimum temperature dropping to −2 °C: in Kuala Forajasaki, the average temperature range in January is around 4 to 10 °C, while in July, the average temperature range is around 15 to 26 °C. Winter temperatures are higher along the northern coast than in the mountainous hinterland. Summers in Forajasaki are quite hot and humid with temperatures exceeding 25 °C in most parts of the country. Forajasaki is the same as in its neighboring country, having four different seasons; spring, summer, autumn and winter. Spring usually occurs in early March to early June, summer from mid-June to mid-September, autumn from late September to mid-November and winter from late November to late February.
Rainfall in Forajasaki is concentrated in late spring to mid-autumn. The north and west coasts and islands are likely to be exposed to strong winds, heavy rains and sometimes flooding may occur.
Government and politics
The Federation of Forajasaki is a federal constitutional monarchy consisting of a federation of eight entities that have different systems either an absolute monarchical system or a democratic system. It is administered by the Supreme Council of the Forajasaki Federation consisting of the ruling Sultan of Kuala Forajasaki, the king or chief executive of the seven entities. A percentage of revenue from each entity is allocated to Forajasaki’s central budget. Each ruler in each entity in the Federation of Forajasaki uses a different title, usually it uses the title of Sultan, King or Sheikh, while the rulers of Bahot and Ghawur use the title of chief executive. It has a legal system based on Western law, although sharia law replaces it in some cases involving citizens who are Umraists.
The President of Forajasaki is a Forajasaki's head of state who is called the Ruler of the State (Yang Menguasai Negara), he is elected by the Supreme Council of the Forajasaki Federation. The current President or Ruler of the State is Ahmad Abdullah Inzun Shah, who is also the Sultan of Kuala Forajasaki. It is likely that the five heads of state in Forajasaki will be elected as Interim Ruler of the State or Acting Ruler of the State. It is stipulated in the constitution of Forajasaki which provides that the Ruler of the State has full executive power. The head of government is a Prime Minister, who heads the cabinet of ministers in the country. Usually, only independent parliamentarians will be elected prime minister. The current Prime Minister is Abdullah Fattah.
The Forajasaki Federal Council of Ministers (Phineaner: Majlis Menteri-Menteri Persekutuan Forajasaki) is the head of the executive branch of government which has been chaired by the Prime Minister as head of government. The Prime Minister, appointed by the Ruler of the State (President) and the Supreme Council of the Forajasaki Federation, appoints ministers in his cabinet.
Foreign relations
- Main article: Foreign relations of Forajasaki
Military
Administrative divisions
The Federation of Forajasaki consists of nine states and two autonomous regions. The states of Kuala Forajasaki, Jagor and Barine are among the three most populous states, with Kuala Forajasaki being the capital and largest city with 28.4 per cent of the population, while Barine and Jagor each have 17.6 per cent of the population, meaning that more than three a fifth of the Forajasaki population lives in the three states. Most of its inhabitants live along the coastal area, including the Jagor's enclave.
State of Sikin is the largest state of Forajasaki, with 54.2 percent of the total area of the country, yet has no coastlines and it is divided into several administrative regions. The two autonomous regions of Forajasaki are Bahot and Ghawur, located between the four main states from north to south. All states in Forajasaki except Sikin, including Bahot and Ghawur have coastlines. The states of Jagor have enclaves, where the Jagor enclave borders the states of Barine and Kuala Forajasaki, the capital of Jagor, Da Toh is located on its southern enclave adjacent to Kuala Forajasaki, while the enclave of Barbara states borders the state of Sikin on the east and two autonomous regions in west side.
The State of Pokok Emas Islands is an archipelago entity located off the coast of Forajasaki and it borders with Phinbellan waters. The entity consists of three main islands (Barack Island, Farahin Island and Tia Island) and several small islands and coral reefs. Several small islands and coral reefs overlap with the border of Forajasakian and Phinbellan waters, there is a possibility of a sovereignty dispute between the two countries, several small islands in the state are close to the waters of Cyberaya and Gordonz territory. The Pokok Emas Islands is an entity that contributes significantly to the Forajasakian oil and tourism industry sector.
Sagiri is a new state establised in October RP 2619, formerly part of the Phinbellan Territory of Soccsksargen, however Sagiri is not a part of Soccsksargen geographically and not part of the Soccsksargen's original geographic regions, this state are part of them historically since RP 2615 until RP 2619. Kuala Sagiri was the capital of the new state.
| Flag | Entity | Capital | Population | Area | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RP 2617 | % | (km2) | (mi2) | % | |||
| Kuala Forajasaki | Kuala Forajasaki | ||||||
| Barine | Kota Batang Rumput | ||||||
| Sikin | Kota Pelampungan | ||||||
| Jagor | Da Toh/Bandar Semarang | ||||||
| Barbara | Borges | ||||||
| Tabui | Bandar Tabui | ||||||
| Shintaro | Pepalih Watik | ||||||
| Pokok Emas Islands | Barack Island | ||||||
| Sagiri | Kuala Sagiri | ||||||
| Bahot | Bandar Batawi | ||||||
| Ghawur | Pasawi | ||||||
| Forajasaki | Kuala Forajasaki | 14,000,300 | 100% | ||||
Human rights
Media
Economy
Business and finance
Oil and gas
Tourism
Transport
Air
Kuala Forajasaki International Airport is the main and only busiest airport in Forajasaki. It is located in the northern part of the state. It is among the main entrances to Forajasaki, and has domestic routes and several international routes to Phinbella only.
Road
The states and autonomous regions on the west and north coasts namely Ghawur, Barine, Kuala Forajasaki, Jagor, Bahot and Barbara have been connected by Highway 1, the main highway in Forajasaki. Kuala Forajasaki, Jagor and Barine are three states with many expressways. The expressway in Forajasaki has a distance of 684 kilometers, and all expressways and its facilities in Forajasaki are operated by an agency known as the Forajasakian Expressway Corporation (FXC) and several concessions under that agency. At the end of RP 2616, a new expressway was built from Kuala Forajasaki to Sikin state and continued to the Oriental Taemhwan border.
Railways
Sea
Energy
Telecomunications
Culture
Education
- Main article: Education in Forajasaki
Demographics
Religion
Umraism is one of the largest and official religions in Forajasaki. The government followed a policy of tolerance for other religions and rarely interfered in the religious activities of non-Umraists.
In the RP 2606 Census of Population and Housing, so far Umraism has reached 55.4 percent, while the first minority religion is Karmaism at 19.8 percent, followed by Nazarene at 9.2 percent. Judaism makes up a community of 7.4 percent of the population, while Krishnism makes up 6.3 percent and Jing folk religions make up 1.3 percent. The remaining 0.6 percent is taken into account by other religions such as animism, Sikhism, folk religion and other belief systems.
Largest city
Languages
Phineaner is the official and national language of Forajasaki, it is likely that the standard of this language could be known as the "Fora language" or the "Forajasakian language". There are about five Phineaner dialects and several Phineaner creoles available in Forajasaki. Common Tongue is the second language and the primary lingua franca in Forajasaki for expatriates residing in the country. Common Tongue knowledge is a requirement for foreign workers to get jobs, except for Phinbellan people (who also want to work at Forajasaki) who use the Phineaner language.