Boriquén: Difference between revisions
| Line 146: | Line 146: | ||
===Judicial=== | ===Judicial=== | ||
The judiciary of the Areyto Boriquén is composed of the the Tribunal de los Bohiques (Tribunals of the Bohiques) as the highest regional court, the Boriquén Court of Appeals as the immediate appellate court, the cacicazgo courts and the yucayeque courts as the two primary trial courts, and several other administrative and special courts, as established by the regional constitution and laws. Judges are known as bohiques in Boriquén. All bohiques in the Areyto Boriquén are appointed to office by the [[King of Nouvelle Alexandrie]], after the Regional Governor and legal professionals in the region nominate them and the Areyto Legislativo confirms them. The Tribunals administers all the courts. | |||
The Tribunal de los Bohiques is composed of the Bohique Supremo and eight other Bohiques Magistrados (Associate Bohiques). The Boriquén Court of Appeals hears all appeals from the circuit courts and, in some cases, directly from the probate courts. Bohiques serve in panels together and decisions are binding regionally. Cases are heard by the Court of Appeals by panels of three judges, who examine the application of the law and not the facts of the case, unless there has been grievous error pertaining to questions of fact. | |||
The cacicazgo courts hear the more serious criminal cases in Boriquén. In addition, they are the appellate court for cases heard in the smaller yucayeque courts. There are 6 cacicazgo courts for each one of the 6 states of Boriquén. Cacicazgo courts have appellate jurisdiction from yucayeque courts and other administrative and special courts courts, as well as from decisions and decrees of regional agencies. | |||
The yucayeque courts hear cases involving less serious criminal offenses, with each municipality (yucayeque) within a state in Boriquén having one. If populations are sparse in some yucayeques, joint yucayeque courts are instituted. Yucayeque courts are trial courts of limited jurisdiction, handling most traffic violations, small claims, misdemeanors, and small civil suits. Yucayeque courts are often responsible for handling the preliminary examination and for setting bail in felony cases. | |||
===Subdivisions=== | ===Subdivisions=== | ||
Revision as of 01:47, 25 January 2024

|
This article or section is a work in progress. The information below may be incomplete, outdated, or subject to change. |
| Region of Boriquén Région de Boriquén Región de Boriquén | |||
| Region of | |||
| |||
| Motto | Utuado Kanaima (Heart of the Spirit Land) | ||
| Anthem | La Boriqueña | ||
| Subdivision | Region | ||
| Capital | Hato Rey | ||
| Largest cities | Hato Rey | ||
| Area | |||
| - Ranked | |||
| Population | 15,337,602 (1718 AN) | ||
| - Ranked | |||
| Viceroy | Cacique Guarionex II | ||
| Taino | Yucahúké Busiri | ||
| Legislature | Kuraka Council | ||
| Established | 1718 AN | ||
| Languages | |||
| Local religion | |||
| Abreviation | BOR | ||
| Time Zone | |||
Boriquén, a Region within the Federation of Nouvelle Alexandrie, is nestled in the verdant southeastern expanses of Keltia, its geographical and cultural uniqueness standing as a testament to its historical significance. The region, spanning vast territories acquired during the transformative Operation Purple Splendor, is home to a diverse population of 15,337,602 residents as of 1718 AN. The bustling capital city of Hato Rey, celebrated for its vibrant cultural scene and historic landmarks, is the region's largest and most populous city. Its Port is among the largest in the Federation.
In contrast, the city of Guánica, with its deep historical and cultural ties to the indigenous Wakara people, serves as the spiritual heart of the region and its second largest city. Revered as the holiest city in the Yukiyu Atabey faith, Guánica stands as an enduring symbol of the Wakara's rich spiritual heritage and the holiest site in Yukiyeyismo. Boriquén's official admission into the Federation in 1718 AN came in the wake of the pivotal ratification and implementation of the Plan de Hato Rey and the Boriquén Admission Act, 1718, solidifying its status within the nation's political and cultural landscape.
Boriquén's history is etched in the annals of time, with archeological evidence revealing a tapestry of indigenous Keltian societies who called the region home thousands of years ago. Of these societies, the resilient Wakara people emerged as a dominant culture, their legacy still resonant in the region's cultural milieu. The tapestry of Boriquén's history is woven with threads of empires, kingdoms, and nations that rose and fell over the centuries. It remained largely unrecognized or subjugated by other Micran countries, and never acquired official recognition from the Micras Cartography Society throughout most of its history. Previously considered part of the vast Keltian Green, Boriquén stood at the crossroads of many historical shifts, cultural exchanges, and conflicts around Lake Cherusken, which shapes the region and is its lifeline.
Etymology
The word "Boriquén" (Borikén) comes from the Wakara language, meaning "Land of the Valiant and Noble Lord". The name comes from the creationist myth of the Yukiyeyismo faith, which is the predominant religion among the Wakara people. Atabey and Yukiyu, the central deities of Yukiyeyismo danced in the cosmic sea, their movements creating ripples and waves. From their dance, the first continents and islands emerged, the first being named Borikén by Atabey, consecrating them as the lands that would become the home of the Wakara people. The word Borikén was later martinized into Boriquén.
History
Background
Operation Purple Splendor
Plan de Hato Rey
Transition to Region, Admission to Federation
A New Region
Geography
Location
Climate
Environment
Administrative Divisions
Politics
The current regional government of Boriquén was established in 1719 AN, after the passage of the Boriquén Admission Act, 1718 and the ratification of the Plan de Hato Rey. All governmental powers are delegated by the Proclamation of Punta Santiago and the Cortes Federales of Nouvelle Alexandrie, with the head of state being the King of Nouvelle Alexandrie. The current regional Constitution was adopted in 1720 AN. The official Wakara name of the regional government is Areyto Boriquén.
Regional government
The Areyto Boriquén is composed of three branches, established by its regional Constitution and in compliance with the Regional and Local Government Organization Act, 1699. The executive is headed by a directly elected Regional Governor of Boriquén, currently Ana Yuisa Caguax of the Wakara People's Party (WPP) since 1723 AN. The legislative branch consists of the unicameral Areyto Legislativo de Boriquén. The Areyto Legislativo presided by the Taino of the Areyto Legislativo, who is currently the Prince of Boriquén, Guarionex II, since 1723 AN. The regional governor and the nitainos are popularly elected every 5 years, with the last election held in 1723. The judicial branch consists of the Tribunal de los Bohiques (Bohique Tribunals), headed by the Bohique Supremo Guacamarí Yarimar. The judges, or bohiques, are appointed to the Tribunals by the King after the Regional Governor and legal professionals in the region nominate them and the Areyto Legislativo confirm them.
Executive
The executive branch of the Areyto Boriquén, consisting of the Regional Governor, Lieutenant Governor, and various secretaries overseeing different departments, forms the Consejo Ejecutivo de Areito Boriquén (Executive Council of Areito Boriquén). The Consejo Ejecutivo is appointed by the Regional Governor at the start of his term and confirmed by the Areyto Legislativo. The Consejo is pivotal in implementing the laws passed by the Areyto Legislativo, managing day-to-day governance of the regional government, and formulating policy for the region of Boriquén.
| Office | Current Officeholder | Term |
|---|---|---|
| Regional Governor | Ana Yuisa Caguax (WPP) | 1723 - |
| Lieutenant Governor | Yaracuy Guaitiao (Independent) | 1723 - |
| Secretary of State | María-Teresa Enríquez (FHP) | 1723 - |
| Attorney-General | Carlos Fontanilla (WPP) | 1723 - |
| Secretary of Economy and Finance | Jorge Eduardo Vargas (WPP) | 1723 - |
| Secretary of Commerce | Aruco Cemi (WPP) | 1723 - |
| Secretary of Education | Rafael Fuentes (WPP) | 1723 - |
| Secretary of Labor | Daniela Lugo (Independent) | 1723 - |
| Secretary of Public Services | Roberto Nuñez Barreto (WPP) | 1723 - |
| Secretary of Health | Ignacio Perez y de Pauta (FHP) | 1723 - |
| Secretary of Culture and Sports | Dra. Élise Anacaona Duval (WPP) | 1723 - |
| Secretary of Agriculture | Carlos Agüeybaná (WPP) | 1723 - |
| Secretary of the Environment | Alexandre Yucayeque (WPP) | 1723 - |
| Secretary of Public Works and Infrastructure | Fernando Tureyro (WPP) | 1723 - |
Legislative
The legislature of the Areyto Boriquén is the unicameral Areyto Legislativo de Boriquén. It has 425 members, called Nitainos. The Taino of the Areyto Legislativo presides over the Areyto Legislativo, elected at the start of every legislative term and can be someone who is not a Nitaino. The Regional Governor can summon the Areyto Legislativo for special sessions, usually reserved for legislation deemed critical for the conduct of regional affairs or the welfare of the people. The Taino also has the power to call the Areyto Legislativo for special sessions as well, but this must be only at the request of two-thirds of the members of the Areyto Legislativo.
| Seat Distribution in the Areyto Legislative of Boriquén (1723 General Elections) | |
|---|---|
| Party | Seats |
| Wakara People's Party (WPP) | 191 |
| Federal Humanist Party (FHP) | 113 |
| Federal Consensus Party (FCP) | 97 |
| Democratic Socialist Party (DSP) | 24 |
Judicial
The judiciary of the Areyto Boriquén is composed of the the Tribunal de los Bohiques (Tribunals of the Bohiques) as the highest regional court, the Boriquén Court of Appeals as the immediate appellate court, the cacicazgo courts and the yucayeque courts as the two primary trial courts, and several other administrative and special courts, as established by the regional constitution and laws. Judges are known as bohiques in Boriquén. All bohiques in the Areyto Boriquén are appointed to office by the King of Nouvelle Alexandrie, after the Regional Governor and legal professionals in the region nominate them and the Areyto Legislativo confirms them. The Tribunals administers all the courts.
The Tribunal de los Bohiques is composed of the Bohique Supremo and eight other Bohiques Magistrados (Associate Bohiques). The Boriquén Court of Appeals hears all appeals from the circuit courts and, in some cases, directly from the probate courts. Bohiques serve in panels together and decisions are binding regionally. Cases are heard by the Court of Appeals by panels of three judges, who examine the application of the law and not the facts of the case, unless there has been grievous error pertaining to questions of fact.
The cacicazgo courts hear the more serious criminal cases in Boriquén. In addition, they are the appellate court for cases heard in the smaller yucayeque courts. There are 6 cacicazgo courts for each one of the 6 states of Boriquén. Cacicazgo courts have appellate jurisdiction from yucayeque courts and other administrative and special courts courts, as well as from decisions and decrees of regional agencies.
The yucayeque courts hear cases involving less serious criminal offenses, with each municipality (yucayeque) within a state in Boriquén having one. If populations are sparse in some yucayeques, joint yucayeque courts are instituted. Yucayeque courts are trial courts of limited jurisdiction, handling most traffic violations, small claims, misdemeanors, and small civil suits. Yucayeque courts are often responsible for handling the preliminary examination and for setting bail in felony cases.
Subdivisions
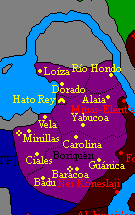
Boriquén is subdivided into 6 states, known as cacicazgos. They are Hato Rey, Loíza, Yayael, Yabucoa, Cemi, and Guaybanex. Each cacicazgo is composed of municipalities called yucayeques. There is only one Special City in Boriquen, the city of Guánica and seat of the cacicazgo of Cemi.
Government Officials
Political Culture
Governor
Article III, Section 1 of the Local Government Act, 1694 provided that, "Every Region as defined by the Proclamation of Punta Santiago, or admitted thereafter into the Federation, shall, after their election in accordance with this Act, thereafter be administered by a Governor, who shall be elected at large by the voters of that Region, and shall serve for a 6-year term. The Governor must be at least 25 years of age, able to read and write, of sound mind, and must be a registered voter of the Region where they intend to run for office."
The Regional and Local Government Organization Act, 1699 repealed Local Government Act, 1694 and Article 7, Section 3 provided that, "Every Region as defined by the Proclamation of Punta Santiago, or admitted thereafter into the Federation, shall, after their election in accordance with this Act, thereafter be administered by a Governor, who shall be elected at large by the voters of that Region, and shall serve for a 5-year term."
Legislature
Article III, Section 3 of the Local Government Act, 1694 established a unicameral legislature, known locally as the [[ ]]. Article III, Section 4, provided that, "The regional legislature which shall be elected at large by the voters of that State shall serve for a 3-year term, and shall have a name and shall be in such form as each Region may provide."
Article XI, Section 3 of the Regional and Local Government Organization Act, 1699 authorized regional legislatures, "to create and charter Special City governments as they may require and provide for their organization", while Section 4, further authorized that regional legislatures "...may provide by general laws for the incorporation of Special Cities. Such laws shall limit their rate taxation for their purposes, and restrict their powers to borrow money and contract debts. Each Special City is granted power to levy other taxes for public purposes, subject to limitations and prohibitions provided by the Proclamation of Punta Santiago or by law."
Article XII, Section 2 of the Regional and Local Government Organization Act, 1699 further empowered regional legislatures, stating that they "...are authorized to create and charter localities below the level of states such as: municipalities, burghs, and other local communities as they may require. Regions may use different terms to refer to a “Municipality”, but the general term for this subdivision shall be generally known as a “Municipality”." Section 3 states that, "Localities shall have such structure as the Regions may require, provided that the boundaries of localities shall be established in consultation with residents of the aforesaid localities and provided that a simple majority of the residents therein assent to the aforesaid establishment of locality by plebiscite or referendum."
Article XII, Section 5 provided regional legislatures with the power of legislative review: "The regional legislatures shall have the power to review legislation adopted by legislative bodies of their localities, and may declare them invalid if found to be in conflict with the law."
Article XII, Section 6 also granted further authority: "Localities created by Regions under authority of this Act may be dissolved by regional legislatures, provided that a simple majority of the residents therein assent to the aforesaid dissolution by plebiscite or referendum."
Court
Article III, Section 2 of the Local Government Act, 1694 created a Regional Court.
Youth Assemblies and Civic Assemblies
Articles V, VII, and VII of the Local Government Act, 1694 instituted Youth Assemblies and Civic Assemblies in "Each existing city, town, and burgh, and such other localities that may be created under authority of this Act", (with subsidiary neighborhood youth and civic assemblies where the adult residents of a locality shall number more than two hundred) which were deliberative bodies composed of all individuals therein resident for at least six months and aged at least twenty-one years. These Youth and Civic Assemblies meet at least once a month to discuss community and youth issues, and adopt such resolutions as its members may see fit. Members of the Youth and Civic Assemblies may present petitions for redress of grievances at meetings of a Civic or Youth Assembly, with the right to speak governed in accordance with the rules of the respective civic or youth assembly.
Law
Local Government
Economy
Fueled by a dynamic blend of traditional and emerging industries, Boriquén boasts a robust and rapidly growing economy. The region is a thriving hub for manufacturing, with sectors spanning from machinery and electronics to textiles and food products contributing significantly to its industrial output. This is further bolstered by the area's natural abundance of raw materials, particularly in metals and minerals, lending strength to its burgeoning mining sector. In the verdant plains and fertile highlands, agriculture plays a pivotal role in the regional economy. The agricultural landscape of Boriquén is richly diverse, producing an array of crops that include rice, quinoa, sugar cane, cacao, vegetables, and fruits, as well as supporting livestock farming. This agricultural productivity not only sustains local food markets and associated agro-based industries but also contributes to the region's export trade.
Boriquén's location on the shores of Lake Cherusken have fostered a prosperous shipping and fishing industry. The fishing communities, steeped in traditions handed down through generations, contribute significantly to the local economy and food supply, while simultaneously supporting an expanding aquaculture sector. Boriquén's strategic geographical location enables it to serve as a crucial nexus between Nouvelle Alexandrie and the rest of the world. The bustling Port of Hato Rey, in particular, see an unending stream of commercial activity, facilitating the movement of goods and stimulating trade. Additionally, the growth of ancillary sectors such as logistics, services, and tourism further enhances the economic vibrancy of the region. With its rich historical tapestry and cultural diversity, Boriquén attracts a steady influx of tourists, leading to substantial revenue and job creation in the hospitality and retail sectors.
Agriculture
Tourism
Hato Rey
Guánica
Energy
Mineral Resources
Transport
Demographics
Ethnic groups
Major cities
Functional urban areas
Language
Religion
Health
Education
Culture
See Also
| |||||