Boriquén: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
}} | }} | ||
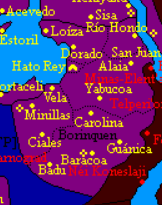
'''Boriquén''' | "'''Boriquén''', a [[Administrative divisions of Nouvelle Alexandrie|Region]] within the Federation of [[Nouvelle Alexandrie]], is nestled in the verdant southeastern expanses of [[Keltia]], its geographical and cultural uniqueness standing as a testament to its historical significance. The region, spanning vast territories acquired during the transformative [[Operation Purple Splendor]], is home to a diverse population of 15,337,602 residents as of {{AN|1718}}. The bustling capital city of [[Hato Rey]], celebrated for its vibrant cultural scene and historic landmarks, is the region's largest and most populous city. Its [[Port of Hato Rey|Port]] is among the largest in the Federation. | ||
Boriquén | In contrast, the city of [[Guánica]], with its deep historical and cultural ties to the indigenous [[Wakara]] people, serves as the spiritual heart of the region and its second largest city. Revered as the holiest city in the [[Wakara]] faith, [[Guánica]] stands as an enduring symbol of the [[Wakara]]'s rich spiritual heritage. Boriquén's official admission into the Federation in {{AN|1718}} came in the wake of the pivotal ratification and implementation of the [[Plan de Hato Rey]] and the [[Boriquén Admission Act, 1718]], solidifying its status within the nation's political and cultural landscape. | ||
Boriquén's history is etched in the annals of time, with archeological evidence revealing a tapestry of indigenous [[Keltia|Keltian]] societies who called the region home thousands of years ago. Of these societies, the resilient [[Wakara|Wakara people]] emerged as a dominant culture, their legacy still resonant in the region's cultural milieu. Historical records, dating as far back as {{AN|1514}}, bear the first official mentions of the term "Wakara". [[Alexandria|Alexandrian]] explorers and diplomats, in their diplomatic cables, briefing reports, and government documents, referred to the indigenous societies as Wakara and [[Wechua]], setting a precedent for identifying the neighboring indigenous [[Keltia|Keltian]] nations. | |||
The tapestry of Boriquén's history is woven with threads of empires, kingdoms, and nations that rose and fell over the centuries, each leaving their indelible mark on the region's cultural and societal development. As part of the vast [[Keltia|Keltian]] [[The Green|Green]] for considerable periods, Boriquén stood at the crossroads of historical shifts and cultural exchanges, shaping the unique and vibrant region it is today. | |||
==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
| Line 51: | Line 55: | ||
===Local Government=== | ===Local Government=== | ||
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
Fueled by a dynamic blend of traditional and emerging industries, Boriquén boasts a robust and rapidly growing economy. The region is a thriving hub for manufacturing, with sectors spanning from machinery and electronics to textiles and food products contributing significantly to its industrial output. This is further bolstered by the area's natural abundance of raw materials, particularly in metals and minerals, lending strength to its burgeoning mining sector. In the verdant plains and fertile highlands, agriculture plays a pivotal role in the regional economy. The agricultural landscape of Boriquén is richly diverse, producing an array of crops that include rice, quinoa, sugar cane, cacao, vegetables, and fruits, as well as supporting livestock farming. This agricultural productivity not only sustains local food markets and associated agro-based industries but also contributes to the region's export trade. | |||
Boriquén's location on the shores of [[Lake Cherusken]] have fostered a prosperous shipping and fishing industry. The fishing communities, steeped in traditions handed down through generations, contribute significantly to the local economy and food supply, while simultaneously supporting an expanding aquaculture sector. Boriquén's strategic geographical location enables it to serve as a crucial nexus between [[Nouvelle Alexandrie]] and the rest of the world. The bustling [[Port of Hato Rey]], in particular, see an unending stream of commercial activity, facilitating the movement of goods and stimulating trade. Additionally, the growth of ancillary sectors such as logistics, services, and tourism further enhances the economic vibrancy of the region. With its rich historical tapestry and cultural diversity, Boriquén attracts a steady influx of tourists, leading to substantial revenue and job creation in the hospitality and retail sectors. | |||
===Agriculture=== | ===Agriculture=== | ||
===Tourism=== | ===Tourism=== | ||
| Line 58: | Line 65: | ||
===Mineral Resources=== | ===Mineral Resources=== | ||
===Transport=== | ===Transport=== | ||
==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
===Ethnic groups=== | ===Ethnic groups=== | ||
Revision as of 03:49, 20 July 2023

|
This article or section is a work in progress. The information below may be incomplete, outdated, or subject to change. |
| Region of Boriquén Région de Boriquén Región de Boriquén | |||
| Region of | |||
| |||
| Motto | Utuado Kanaima (Heart of the Spirit Land) | ||
| Anthem | La Boriqueña | ||
| Subdivision | Region | ||
| Capital | Hato Rey | ||
| Largest cities | Hato Rey | ||
| Area | |||
| - Ranked | |||
| Population | 15,337,602 (1718 AN) | ||
| - Ranked | |||
| Viceroy | Cacique Guarionex II | ||
| Taino | Yucahúké Busiri | ||
| Legislature | Kuraka Council | ||
| Established | 1718 AN | ||
| Languages | |||
| Local religion | |||
| Abreviation | BOR | ||
| Time Zone | |||
"Boriquén, a Region within the Federation of Nouvelle Alexandrie, is nestled in the verdant southeastern expanses of Keltia, its geographical and cultural uniqueness standing as a testament to its historical significance. The region, spanning vast territories acquired during the transformative Operation Purple Splendor, is home to a diverse population of 15,337,602 residents as of 1718 AN. The bustling capital city of Hato Rey, celebrated for its vibrant cultural scene and historic landmarks, is the region's largest and most populous city. Its Port is among the largest in the Federation.
In contrast, the city of Guánica, with its deep historical and cultural ties to the indigenous Wakara people, serves as the spiritual heart of the region and its second largest city. Revered as the holiest city in the Wakara faith, Guánica stands as an enduring symbol of the Wakara's rich spiritual heritage. Boriquén's official admission into the Federation in 1718 AN came in the wake of the pivotal ratification and implementation of the Plan de Hato Rey and the Boriquén Admission Act, 1718, solidifying its status within the nation's political and cultural landscape.
Boriquén's history is etched in the annals of time, with archeological evidence revealing a tapestry of indigenous Keltian societies who called the region home thousands of years ago. Of these societies, the resilient Wakara people emerged as a dominant culture, their legacy still resonant in the region's cultural milieu. Historical records, dating as far back as 1514 AN, bear the first official mentions of the term "Wakara". Alexandrian explorers and diplomats, in their diplomatic cables, briefing reports, and government documents, referred to the indigenous societies as Wakara and Wechua, setting a precedent for identifying the neighboring indigenous Keltian nations.
The tapestry of Boriquén's history is woven with threads of empires, kingdoms, and nations that rose and fell over the centuries, each leaving their indelible mark on the region's cultural and societal development. As part of the vast Keltian Green for considerable periods, Boriquén stood at the crossroads of historical shifts and cultural exchanges, shaping the unique and vibrant region it is today.
Etymology
History
Background
Operation Purple Splendor
Plan de Hato Rey
Transition to Region, Admission to Federation
A New Region
Geography
Location
Climate
Environment
Administrative Divisions
Politics
Government Officials
Political Culture
Law
Local Government
Economy
Fueled by a dynamic blend of traditional and emerging industries, Boriquén boasts a robust and rapidly growing economy. The region is a thriving hub for manufacturing, with sectors spanning from machinery and electronics to textiles and food products contributing significantly to its industrial output. This is further bolstered by the area's natural abundance of raw materials, particularly in metals and minerals, lending strength to its burgeoning mining sector. In the verdant plains and fertile highlands, agriculture plays a pivotal role in the regional economy. The agricultural landscape of Boriquén is richly diverse, producing an array of crops that include rice, quinoa, sugar cane, cacao, vegetables, and fruits, as well as supporting livestock farming. This agricultural productivity not only sustains local food markets and associated agro-based industries but also contributes to the region's export trade.
Boriquén's location on the shores of Lake Cherusken have fostered a prosperous shipping and fishing industry. The fishing communities, steeped in traditions handed down through generations, contribute significantly to the local economy and food supply, while simultaneously supporting an expanding aquaculture sector. Boriquén's strategic geographical location enables it to serve as a crucial nexus between Nouvelle Alexandrie and the rest of the world. The bustling Port of Hato Rey, in particular, see an unending stream of commercial activity, facilitating the movement of goods and stimulating trade. Additionally, the growth of ancillary sectors such as logistics, services, and tourism further enhances the economic vibrancy of the region. With its rich historical tapestry and cultural diversity, Boriquén attracts a steady influx of tourists, leading to substantial revenue and job creation in the hospitality and retail sectors.
Agriculture
Tourism
Hato Rey
Guánica
Energy
Mineral Resources
Transport
Demographics
Ethnic groups
Major cities
Functional urban areas
Language
Religion
Health
Education
Culture
See Also
| |||||